Epigenetic mechanisms underlying sex differences in the brain and behavior
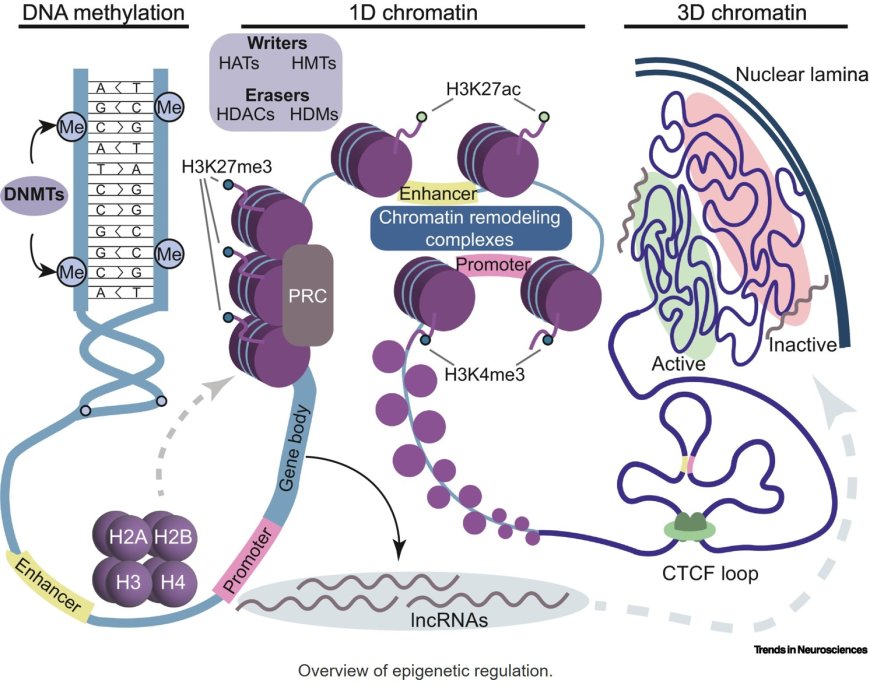
Sex differences in the brain are reflected at the molecular, structural, and behavioral levels, and are observed across brain disorders.
Brain sexual differentiation is a dynamic process throughout life, resulting from interactions of gonadal hormones, sex chromosomes, and the environment.
Studies of sex-specific factors, such as perinatal testosterone exposure in males and the estrous cycle in females, show clear evidence that epigenetic mechanisms drive sex differences in the brain and behavior.
Studies of environmental impact on the brain epigenome across the lifespan have also revealed important sex differences but with more limited mechanistic insights.
Future neuro-epigenetic studies incorporating sex-related variables and better targeted, higher-resolution approaches are hoped to maximize the benefit of insights gained from basic research for people across genders.
https://www.cell.com/trends/neurosciences/fulltext/S0166-2236(23)00225-4