Extreme lifespan multiomics
Recent studies suggest that the steady rise in life expectancy observed over the past 200 years has now stagnated. Data indicate that a limit has been reached, and that medical and healthcare advances no longer affect longevity in developed countries as they did in previous decades. Today, ageing itself, rather than disease, is the real frontier of human longevity. But what exactly is ageing? And can it be addressed in the same way as a disease?
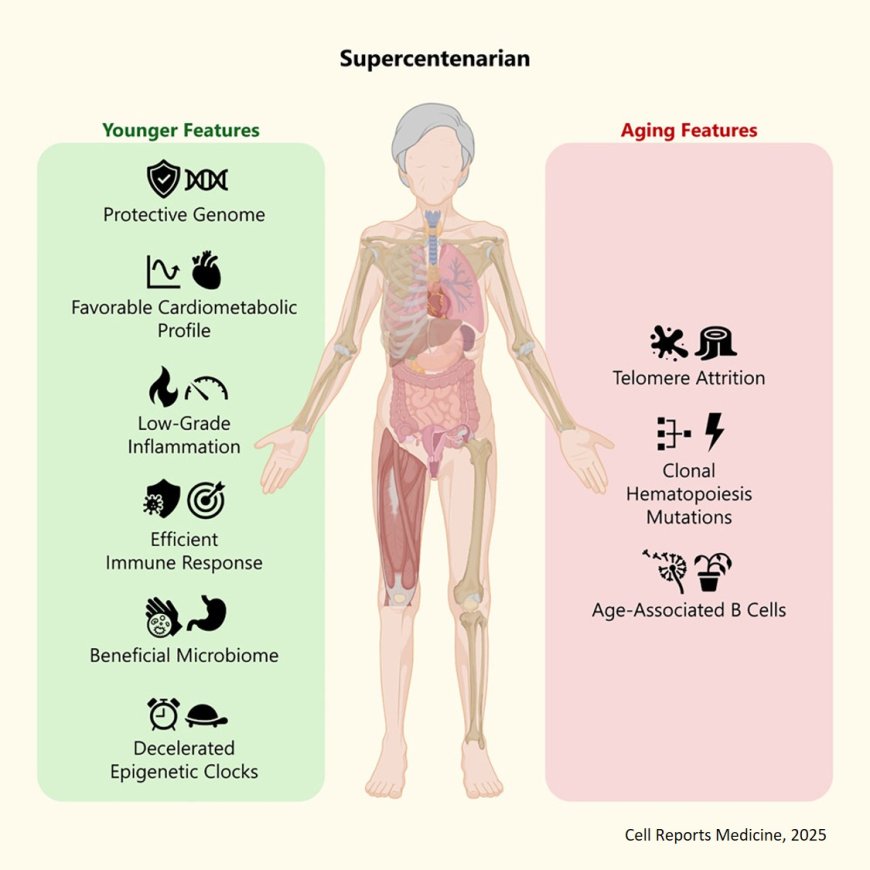
A research team has just published the final peer-reviewed data from the study of the longest-lived person ever recorded, who far exceeded 117 years: the Catalan woman Maria Branyas. The analysis, based on samples obtained using minimally invasive techniques, takes a multi-omic approach with genomic, proteomic, epigenomic, metabolomic and microbiomic technologies, and represents the most exhaustive study ever undertaken on a supercentenarian.
In the paper, published in the prestigious journal Cell Reports Medicine, the international and multidisciplinary team explains that individuals who reach supercentenarian age do not do so through a general delay in ageing but, as the author notes, thanks to a “fascinating duality: the simultaneous presence of signals of extreme ageing and of healthy longevity.”
Although the team detected unmistakable signs of ageing, such as very short telomeres (the ends of chromosomes), a pro-inflammatory immune system, and an aged population of B lymphocytes, Branyas also had genetic characteristics associated to neuroprotection and cardioprotection, genuinely low inflammatory levels, a microbiome dominated by beneficial bifidobacteria, and a biological age younger than her chronological age, as determined by epigenetic markers.
Since ageing of the blood system is known to be closely linked to a higher incidence of incurable blood cancers such as leukaemia and myelodysplastic syndromes, the insights gained from this supercentenarian study may also provide valuable clues for deepening our understanding of these haematological conditions and of the patients affected by them.
The absence of serious disease makes this the first study in which ageing can be clearly distinguished from illness, offering a comprehensive view of the effects of ageing on the human body and perhaps pointing to ways to counteract them. Although it is still too early to link specific biological characteristics to specific habits, the researchers note that a healthy diet, a stimulating and diverse social network, and the absence of toxic habits are factors worth considering when explaining for Mrs Branyas’s exceptional longevity.
With this detailed perspective on extreme ageing, researchers worldwide will be able to better understand this natural process and to propose strategies to address it specifically, in the same way that a disease would be treated. In fact, epigenetic therapies and drugs specifically designed to combat senescence already exist in the field of oncology, aspects that are directly related to biological ageing. Who knows if, in the future, those same tools will be responsible for pushing life expectancy forward once again, after its current plateau.
https://www.cell.com/cell-reports-medicine/fulltext/S2666-3791(25)00441-0