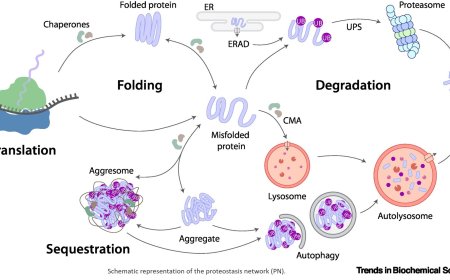
Inter-organ communication in metabolism and aging
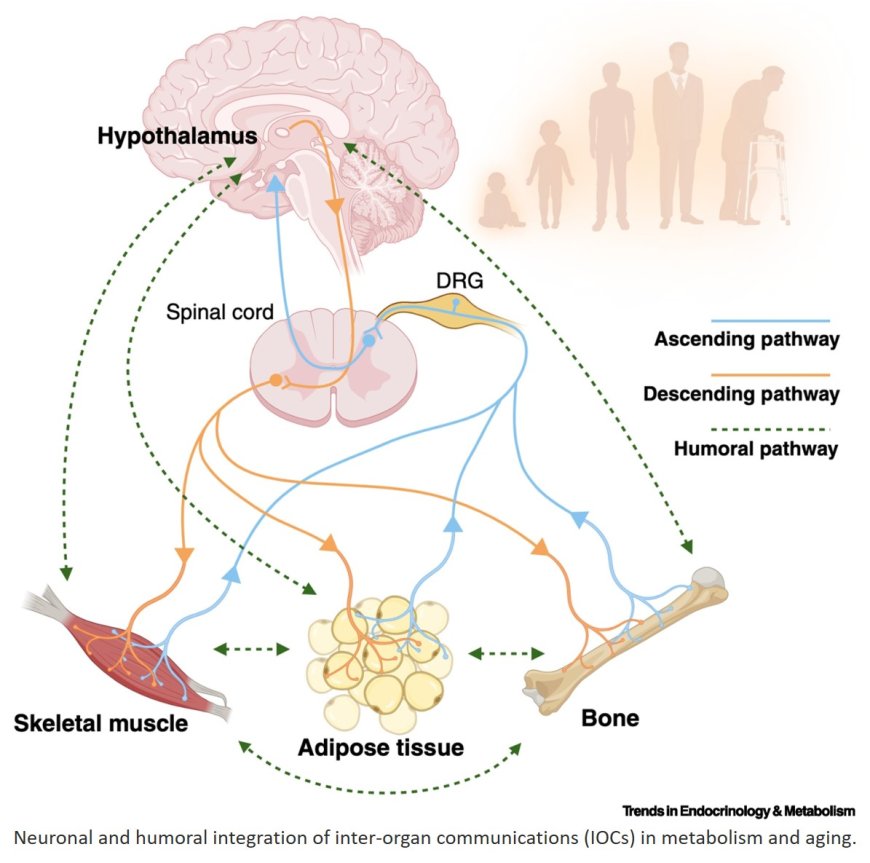
Adipose tissues, skeletal muscle, and bone, traditionally categorized as nonendocrine organs, send humoral signals to others to maintain metabolic homeostasis.
Humoral factors, such as hormones, cytokines, microRNAs, metabolites, and mitochondrial signaling, contribute to metabolic health and aging regulation through inter-organ communication (IOC).
Neuronal integration of IOC by the hypothalamus is a critical contributor to metabolism and aging.
https://www.cell.com/trends/endocrinology-metabolism/fulltext/S1043-2760(24)00320-5