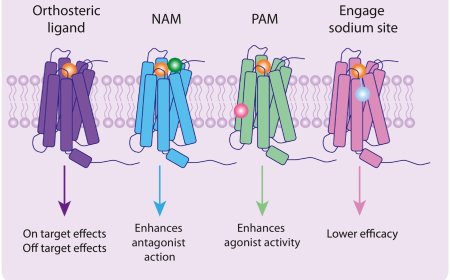
Mechanism of tumor immune escape during p53 inactivation
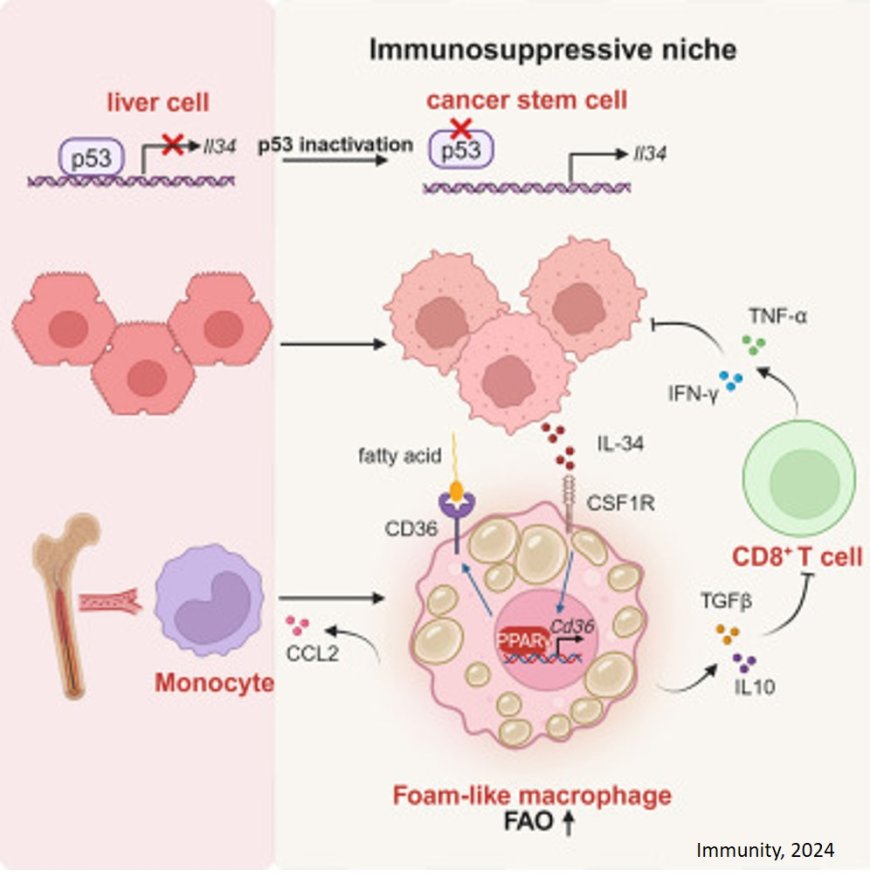
How p53 modulates the immune landscape for immune escape remains elusive.
The researchers report that Il34 is a gene transcriptionally repressed by p53, and p53 loss resulted in IL-34 secretion by cancer stem cells (CSCs).
They also show that IL-34-acts via CD36-axis-to activate tumor associated macrophages (TAMs) to promote tumor immune escape by suppressing T cell-mediated antitumor immunity.
When authors blocked IL-34-CD36 axis, it elicited antitumor immunity that synergized with anti-PD-1 immunotherapy, leading to a complete response.
https://www.cell.com/immunity/fulltext/S1074-7613(24)00415-1