How protein arginine methyltransferase 7 linked to schizophrenia
The pathogenic mechanisms of numerous genomic loci linked to schizophrenia (SCZ) identified via genome-wide association studies (GWASs) is not clearly understood..
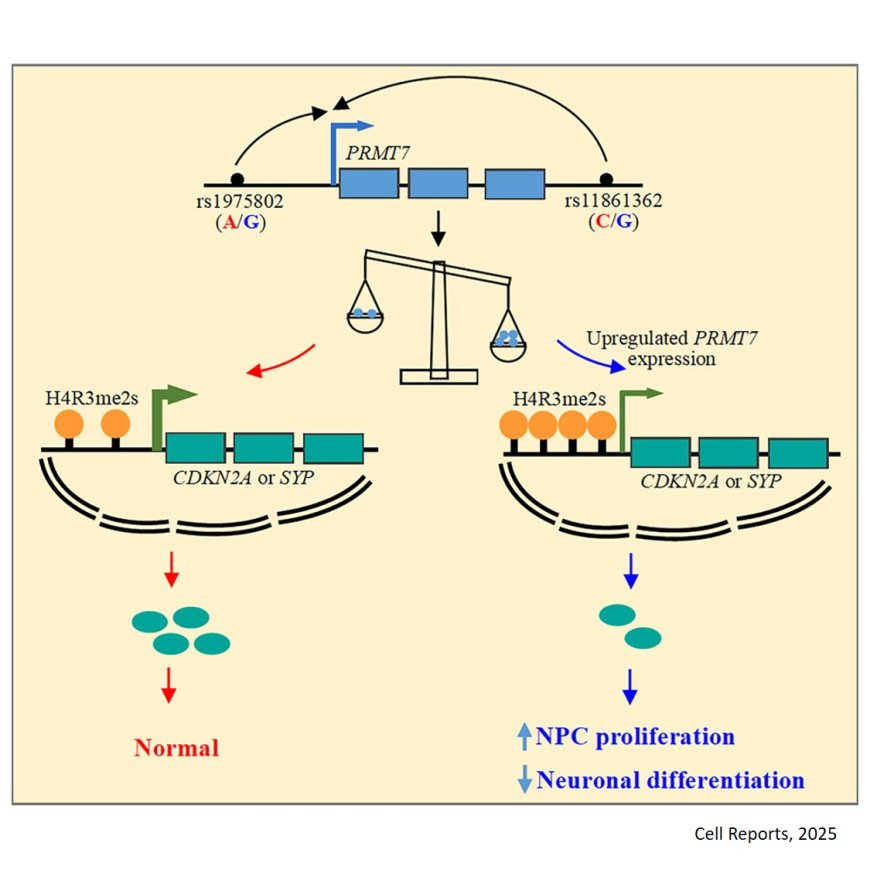
The researchers documented that protein arginine methyltransferase 7 (PRMT7) is a functional target of SCZ risk SNPs at 16q22.1.
They further uncovered that PRMT7 dysregulation resulted in decreased neural progenitor cell (NPC) proliferation, increased neuronal differentiation, and also led to longer neurites in these neurons. overexpressing PRMT7 enhanced NPC proliferation and reduced neuronal differentiation.
The authors show that PRMT7 regulates by impacting the expression of genes related to the cell cycle and neuronal function such as CDKN2A and SYP, via symmetrical di-methylation at arginine 3 of histone 4 (H4R3me2s) modification in their promoters as these genes have a stronger association with SCZ compared to other mental disorders.
https://www.cell.com/cell-reports/fulltext/S2211-1247(25)00050-6