A single-cell atlas of sexual development in Plasmodium falciparum
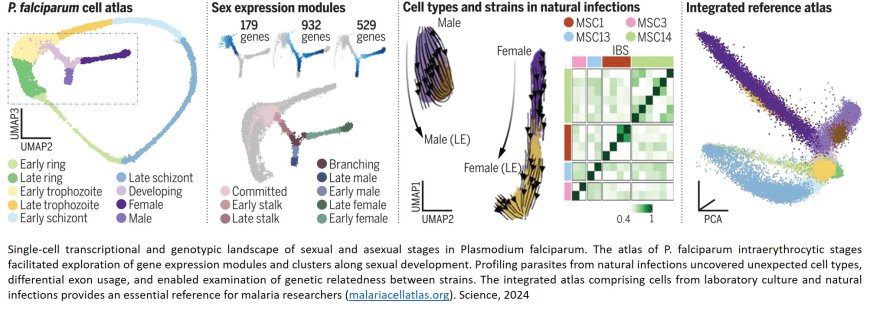
For the first time, the developmental stages of the deadliest human malaria parasite have been mapped in high resolution, allowing researchers to understand this ever-adapting adversary in more detail than previously possible.
The study, published in Science, details the critical developmental stages of the malaria parasite, Plasmodium falciparum, using single-cell RNA sequencing. This gives detailed information on the life stages of this parasite as it matures, changing from an asexual state to a sexual state, which is necessary before the parasite can be transmitted to mosquitoes.
The Atlas provides information for researchers worldwide to investigate and generate tools to track the disease.
The novel insights accessible through the Malaria Cell Atlas can also help identify new ways to block the parasite’s development, including through new drugs or vaccines that can prevent transmission.
Malaria is a life-threatening disease with an estimated 249 million cases and 608,000 deaths globally in 20222. It is caused by the Plasmodium parasite, with P. falciparum being the deadliest type of this parasite and the most prevalent on the African continent2.
P. falciparum is a single-celled parasite that evolves quickly, making it difficult to develop long-lasting and effective diagnostics, drugs and vaccines to protect against it. Malaria parasites have a huge amount of genetic diversity and people are frequently infected with multiple different parasite strains. In Mali, around 80 per cent of people infected with malaria carry multiple genetically distinct parasite strains3.
Malaria parasites are found in either an asexual or sexually developed form in the human host. Asexual replication in humans is what causes the symptoms of malaria, but to transmit, parasites have to develop and become either a male or female reproductive cell, known as a gametocyte.
Sexual commitment and development are controlled by transcription factors, which are proteins that regulate gene activity. The mature sexual forms of the parasite circulate in the bloodstream until they are taken up by mosquitoes.
In the latest research, the researchers used both long-read and short-read single-cell RNA sequencing to map the sexual development stages of P. falciparum in the laboratory. This allowed them to track the gene expression levels and highlight which genes are involved in each stage of the process.
The team then applied this approach to parasites from blood samples collected from four people naturally infected with malaria. This is the first time that these technologies have been applied to real-time infection strains at such a high resolution.
By comparing the laboratory data with the natural infection data, the researchers found parasite cell types not previously seen in laboratory strains, highlighting the importance of real-world data.
The team compared different natural P. falciparum strains within each donor to identify genes of interest.
Some of the genes that were overexpressed in particular strains in the sexual development stages are involved in the survival of the parasite in the ito, including one that plays a role in dampening mosquito immunity. The next step will be to assess the impact these genes have on transmission.
A co-first author said: “This is the first time that we have been able to map the sexual development stages of malaria parasites in both laboratory and natural strains, allowing us to gain deeper insight into the similarities and differences. Our research uncovered new biology present in the naturally occurring strains that are not seen in laboratory strains, improving our understanding of how malaria develops and spreads.”
Another, co-first author said: “Our research adds to the growing Malaria Cell Atlas, giving a high-quality, open-access genomic resource for researchers worldwide. This high-resolution atlas can be used by scientists to gain a clear understanding of the genes they are investigating, combine research efforts, and help us more effectively prevent, control, and treat malaria. Working together as a scientific community is the only way we are going to successfully control and treat malaria.”
Another co-author said: “Malaria has a huge global impact, affecting millions of people each year, and attempts to control and treat the disease are quickly overcome by the parasite. Understanding more about the parasite’s life cycle, the genes involved, and the factors that control these, can be vital to ongoing malaria research. Our research highlights key points in the sexual development of the parasite, which if targeted in future drug development could break the cycle of transmission and help minimise the spread.”
The senior author said: “This new focus of the Malaria Cell Atlas project on natural infections coincides with malaria vaccines being used for the first time and a continued rise of drug resistance. Single-cell RNA sequencing gives us a window