A way to modulate scarring in spinal cord injury
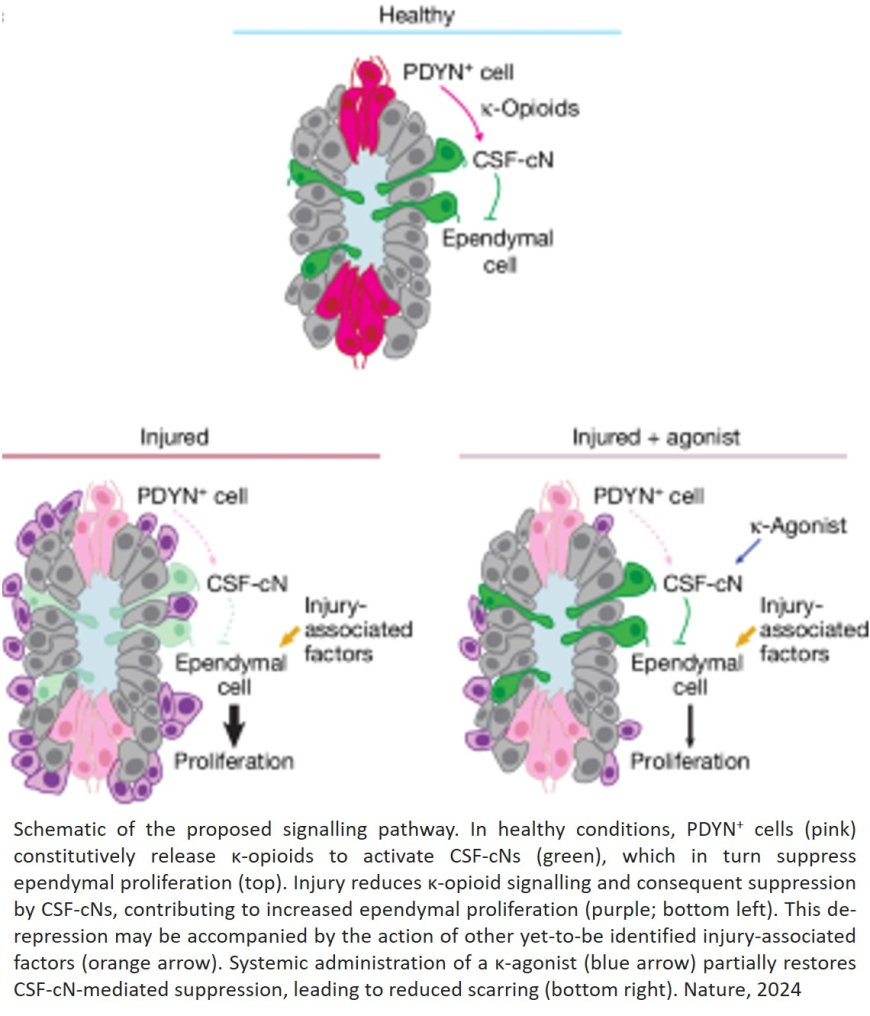
After a spinal cord injury, nearby cells quickly rush to action, forming protective scar tissue around the damaged area to stabilize and protect it. But over time, too much scarring can prevent nerves from regenerating, impeding the healing process and leading to permanent nerve damage, loss of sensation or paralysis.
Now, researchers have discovered how a rarely studied cell type controls the formation of scar tissue in spinal cord injuries. Activating a molecular pathway within these cells, the team showed in mice, lets them control levels of spinal cord scarring. The new research appears in Nature.
“By illuminating the basic signaling biology behind spinal cord scarring, these findings raise the possibility of one day being able to pharmacologically fine-tune the extent of that scarring,” said the senior author of the new paper.
Spinal cord injuries — caused by physical trauma such as vehicle accidents, falls, or sports collisions — can damage the nerves that run down the length of the spinal cord and coordinate messages between the brain and the rest of the body. Treatments largely revolve around surgery or braces to stabilize the spine, drugs to control pain and swelling and physical therapy.
The authors were studying the function of a poorly understood group of neurons, called cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)-contacting neurons. These neurons are found along the hollow channel that runs through the center of the cord, and they extend into the spinal fluid that fills the channel.
The team developed a new method to label these neurons, isolate them and measure which genes were active in the cells. That led them to discover that the cells express a receptor that senses κ-opioids, which are naturally produced by the human body.
The group went on to identify the spinal cord cells that produce κ-opioids, and show how the molecules excite the CSF-contacting neurons.
Further experiments revealed that signaling through these κ-opioids decreased in the aftermath of a spinal cord injury, transforming nearby cells into scar tissue for protection.
The researchers tried delivering extra κ-opioids to the mice, and the scarring was reduced; but the spinal cord injuries were more severe, and the mice did not recover their motor coordination as well.
“κ-opioids might give us a way, after a spinal cord injury, to pharmacologically modulate the fine balance between producing enough scar tissue and having excessive scarring,” said the first author of the new paper.
Importantly, κ-opioids are different from commercial opioid drugs such as oxycodone and hydrocodone, and generally not addictive.
Scientists must do more work to understand why κ-opioid levels drop after spinal cord injuries, as well as what the ideal levels of scarring are to support optimal healing. Further preclinical studies also would be required before testing κ-opioid-related drugs in humans with spinal cord injuries.
The senior author said the new findings underscore the importance of carrying out basic scientific research on how various cell types and signaling molecules work.
“We were not looking for a way to control spinal cord healing,” the author said. “This came out of asking questions about this mysterious cell type, and then running into a mechanism that is both biologically interesting and could eventually have some therapeutic potential.”