Alzheimer’s therapeutics
Alzheimer's therapeutics aim to manage symptoms, slow disease progression, and improve quality of life for individuals with Alzheimer's disease. Current treatments focus on symptom relief, while emerging therapies target disease-modifying strategies.
Symptomatic Treatments
1. Cholinesterase inhibitors: Donepezil, rivastigmine, and galantamine increase acetylcholine levels, improving cognitive symptoms.
2. Memantine: An N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptor antagonist, memantine helps manage moderate to severe Alzheimer's symptoms.
3. Combination therapy: Combining cholinesterase inhibitors with memantine may provide additional benefits.
Disease-Modifying Therapies (DMTs)
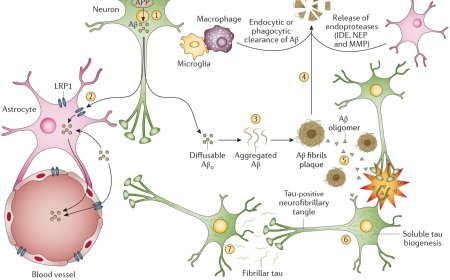
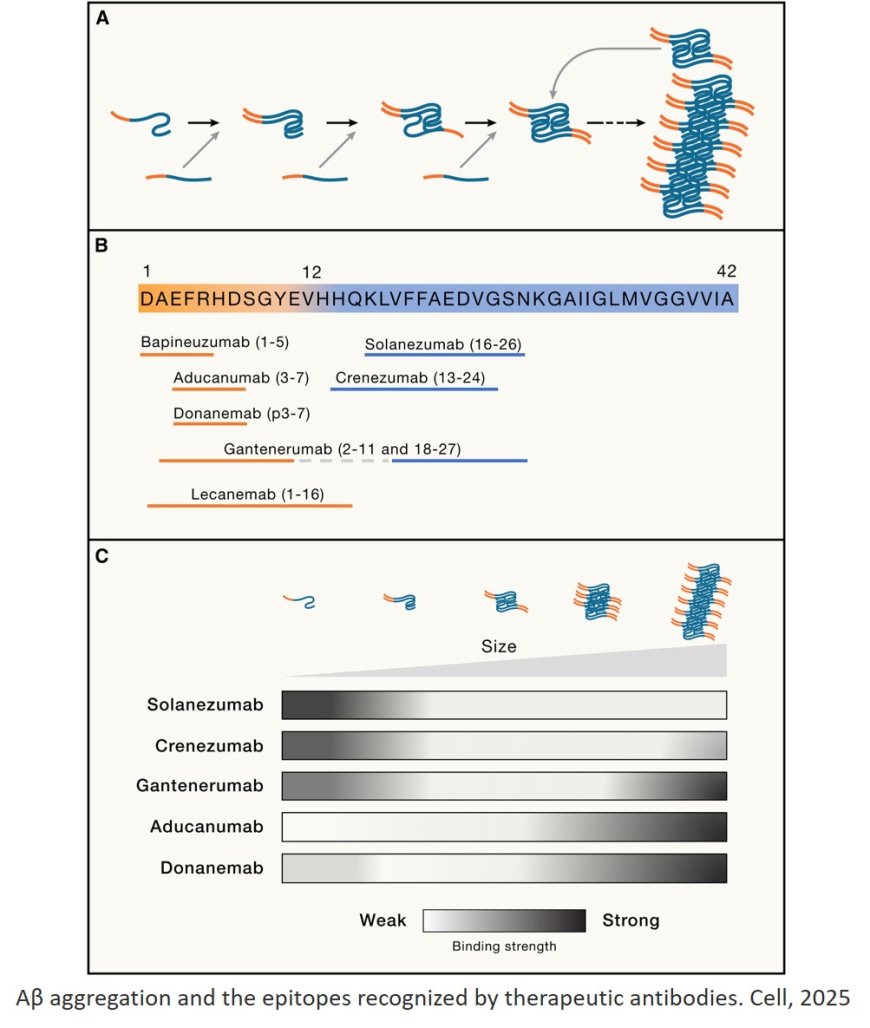
1. Amyloid-targeting therapies: Aducanumab, gantenerumab, and solanezumab aim to reduce amyloid-β plaques.
2. Tau-targeting therapies*: Tau-targeting antibodies, such as gosuranemab, aim to reduce tau protein aggregates.
3. BACE inhibitors: Beta-secretase inhibitors, like verubecestat, aim to reduce amyloid-β production.
4. Gamma-secretase inhibitors: These therapies aim to reduce amyloid-β production by inhibiting gamma-secretase.
Emerging Therapies
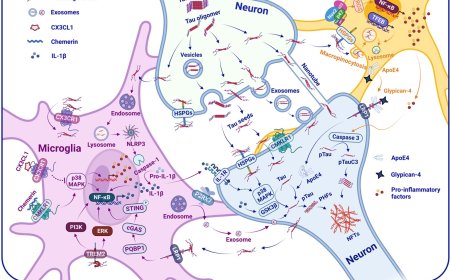
1. Immunotherapies: Active and passive immunotherapies aim to remove amyloid-β and tau proteins.
2. Stem cell therapies: Stem cell-based approaches aim to promote neuroregeneration and repair.
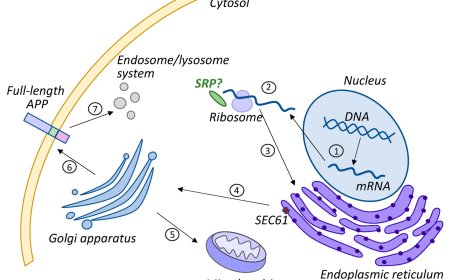
3. Gene therapies: Gene therapies aim to modify or replace genes involved in Alzheimer's disease.
4. Small molecule therapies: Small molecule therapies target various pathways, including amyloid-β, tau, and inflammation.
Lifestyle Interventions
1. Cognitive training: Cognitive training programs aim to improve cognitive function and slow decline.
2. Physical exercise: Regular physical exercise has been shown to improve cognitive function and reduce dementia risk.
3. Social engagement: Social engagement and support have been linked to improved cognitive health.
4. Dietary interventions: Certain diets, such as the Mediterranean diet, may help reduce dementia risk.
Future Directions
1. Personalized medicine: Tailoring treatments to individual genetic profiles and disease characteristics.
2. Combination therapies: Combining multiple treatments to target different disease pathways.
3. Early intervention: Identifying and treating Alzheimer's disease at earlier stages to slow progression.
4. Biomarker development: Developing biomarkers to diagnose and monitor Alzheimer's disease more accurately.
https://www.cell.com/cell/fulltext/S0092-8674(23)00910-8
https://sciencemission.com/Alzheimer%E2%80%99s-disease--immunotherapy