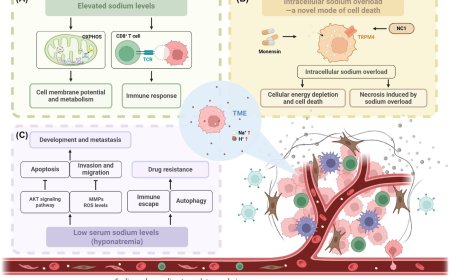
Brain circuit regulating methamphetamine-associated memory
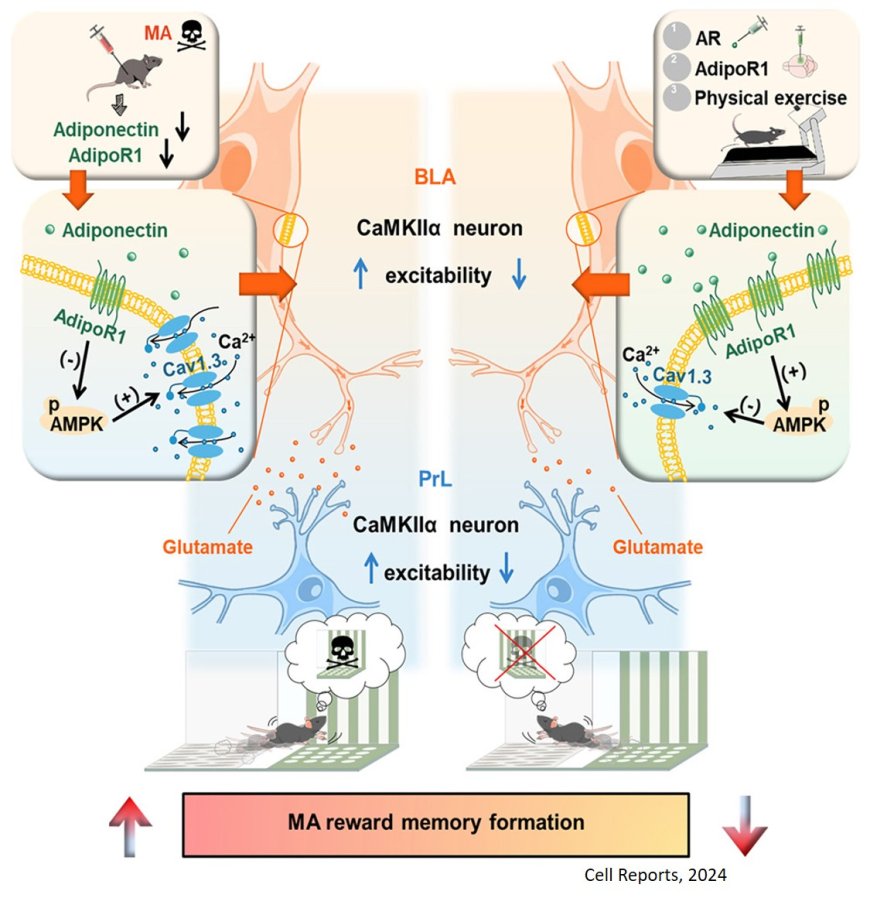
The neural networks and molecular mechanisms orchestrating methamphetamine (MA)-associated memories remain poorly understood.
The researchers reveal the critical roles of Adiponectin receptor 1 (AdipoR1)97 in the basolateral amygdala (BLA) that regulate MA reward memory and suppression of BLA -CaMKIIα neuron activity.
The authors found an association between the excitatory circuit from the BLA to the prelimbic cortex (PrL) and the integration of MA-induced rewards with environmental cues. Phosphorylated AMPK (p-AMPK)/Cav1.3 signaling pathway mediates the modulatory effects of AdipoR1 in PrL-projecting BLA CaMKIIα neurons on the formation of MA reward memories.
They show that AdipoR1 signaling is modulated by physical exercise as an alternative intervention strategy for MA addiction, presenting a potential target for managing MA use disorders.
https://www.cell.com/cell-reports/fulltext/S2211-1247(24)01425-6