Breastfeeding shapes infant’s microbes and promotes lung health
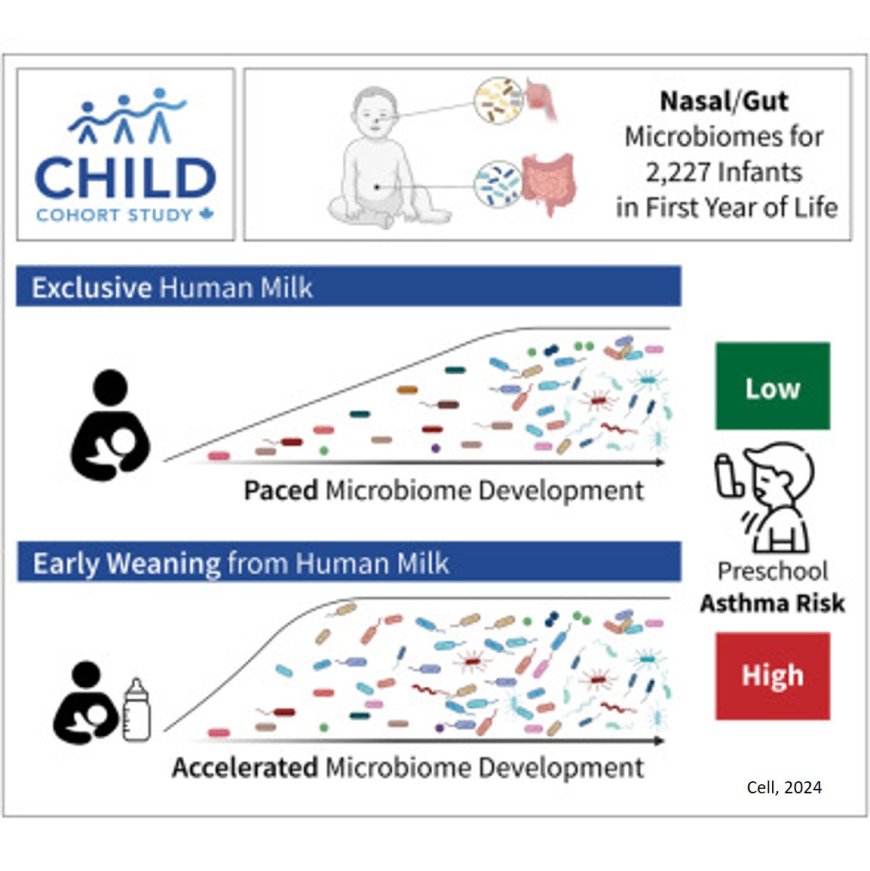
Human breast milk regulates a baby’s mix of microbes, or microbiome, during the infant’s first year of life. This in turn lowers the child’s risk of developing asthma, a new study shows.
The study results showed that breastfeeding beyond three months supports the gradual maturation of the microbiome in the infant’s digestive system and nasal cavity, the upper part of the respiratory tract. Conversely, stopping breastfeeding earlier than three months disrupts the paced development of the microbiome and was linked to a higher risk of preschool asthma.
Some components in breast milk, such as complex sugars called human milk oligosaccharides, can only be broken down with the help of certain microbes. This provides a competitive advantage to microbes capable of digesting these sugars. By contrast, infants who are weaned earlier than three months from breast milk and who then rely solely on formula feeding, become home to a different set of microbes — ones that will help the infant to digest the components in formula. While many of these microbes that thrive on formula do eventually end up in all babies, the researchers showed that their early arrival is linked to an increased risk of asthma.
“Just as a pacemaker regulates the rhythm of the heart, breastfeeding and human milk set the pace and sequence for microbial colonization in the infant’s gut and nasal cavity, ensuring that this process occurs in an orderly and timely manner,” said the study co-senior investigator. “Healthy microbiome development is not only about having the right microbes. They also need to arrive in the right order at the right time,” said the author.
Another key study finding was that the bacterial species called Ruminococcus gnavus appeared much sooner in the guts of children who were weaned early from breast milk than in those of children who were exclusively breastfed. The bacterium is known to be involved in the production of molecules called short-chain fatty acids, and the formation and breakdown of the amino acid tryptophan. Both tryptophan and its metabolites have been linked to immune system regulation and disruption in previous research, including an increased risk of asthma. The study authors noted that beyond aiding in digestion, an infant’s microbiome plays a crucial role in the immune system’s development.
Publishing in the journal Cell, the study tracked the ebb and flow of microbes in the guts and noses of infants during the first year of life, as well as details on breastfeeding and the composition of their mothers’ milk. All the children and their mothers were participating in the CHILD Cohort Study, a long-term research project that has been studying the same 3,500 Canadian children at different stages of life from the womb well into adolescence.
The data provided by the CHILD Cohort Study enabled researchers to detangle the impact of breastfeeding on an infant’s microbiome from a range of other environmental factors, including prenatal smoke exposure, antibiotics, and the mother’s asthma history.
Even when these factors were accounted for, they found that breastfeeding duration remained a powerful determinant for the child’s microbial makeup over time. They also used these microbial dynamics and data on milk components to train a machine-learning model that accurately predicted asthma years in advance. Finally, they created a statistical model to learn causal relationships, which showed that the primary way breastfeeding reduces asthma risk is through shaping the infant’s microbiome.
“The algorithms we developed provide valuable insights into microbial dynamics during an infant’s first year of life and how these microbes interacted with the infant,” said the author. “These insights allowed us to move beyond identifying associations, enhancing our ability to make predictions and explore causal relationships.
“Our research highlights the profound impact of breastfeeding on the infant microbiome and breastfeeding’s essential role in supporting respiratory health. By uncovering the mechanisms behind the protective effects of breast milk, as demonstrated in this study, we aim to inform national guidelines on breastfeeding and weaning from breast milk in a data-driven manner.
“With further research, our findings could also contribute to developing strategies to prevent asthma in children who cannot be breastfed for at least three months,” the author added.