Role of CXCR3-mediated natural killer cell infiltration in intracerebral haemorrhage
Neurological damage from inflammation plays a critical role in intracerebral haemorrhage (ICH) in the early phase.
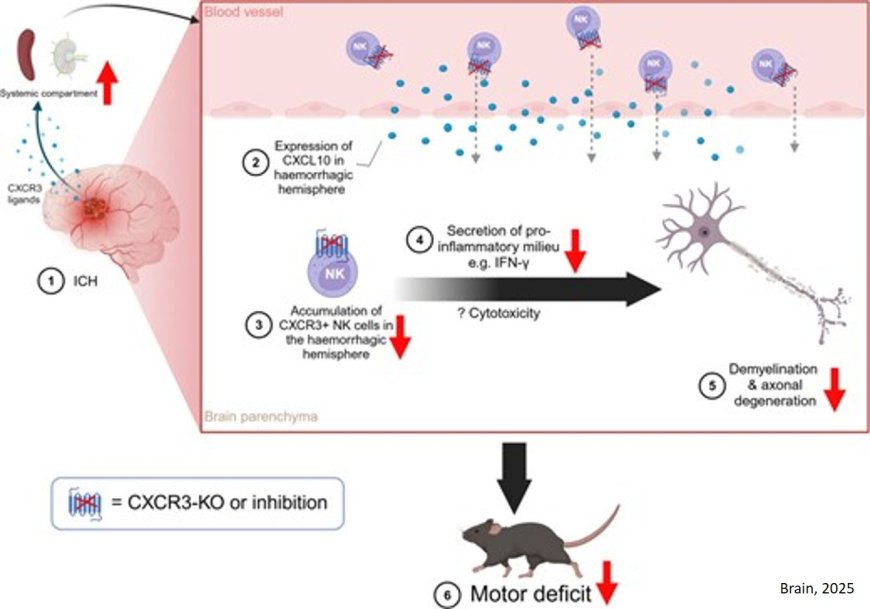
Exacerbating neurological dysfunction is the CXC chemokine receptor 3 (CXCR3)-chemokine system that mediates neuroimmune crosstalk. CXCR3 is expressed by natural killer (NK) cells and its role in ICH is evaluated in this study.
The authors demonstrate for the first time that CXCR3 facilitates the migration of NK cells from the systemic compartment into the haemorrhagic brain causing ICH-related neurological injury. They also found upregulation of CXCR3 expression in the peri-haematomal region including the white matter tracts.
Knock-out of CXCR3 deficiency resulted in reduced recruitment of NK cells expressing interferon-gamma (IFN-γ), and better corticospinal tract integrity in the cervical spinal cord and improved neurological outcomes. In addition, administration of a CXCR3 antagonist (AMG487), reversed neurological damage.
https://academic.oup.com/brain/advance-article/doi/10.1093/brain/awaf108/8090332
https://sciencemission.com/CXCR3-mediated-natural-killer-in-ICH