Controlling insulin sensitivity in muscle by endothelial cells
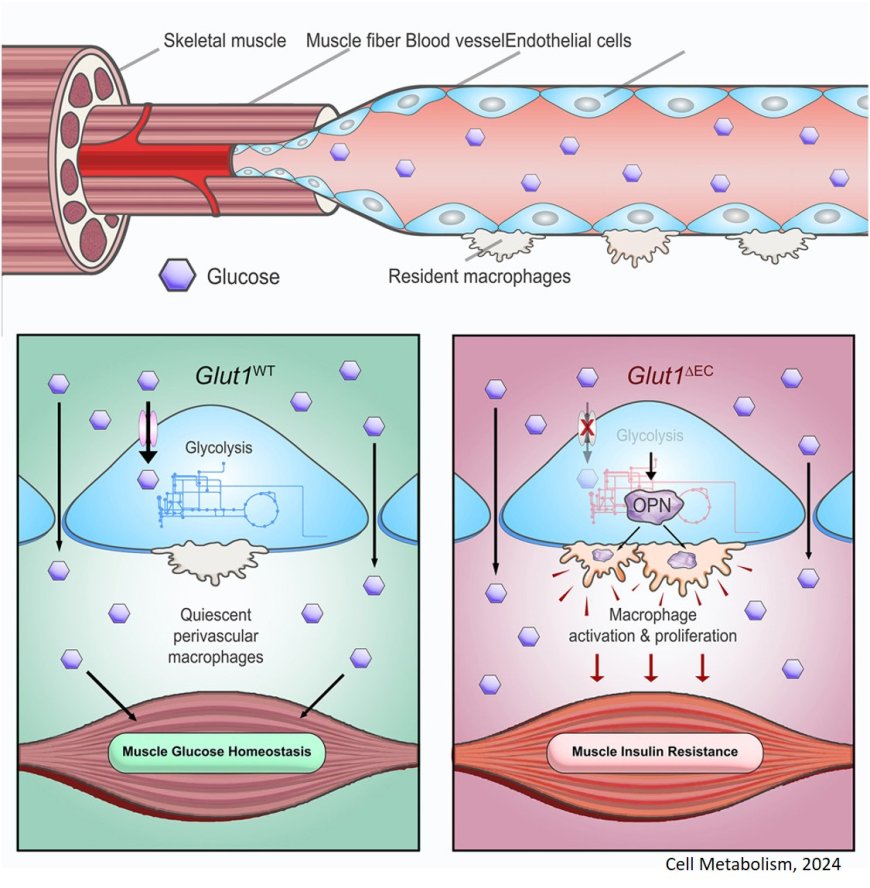
Endothelial cells (EC) form the lining of the blood vessel but its role in glucose homeostasis is not clearly known.
The researchers found that endothelial glucose transporter 1 (GLUT1) regulates muscle insulin sensitivity via vascular metabolic control of muscle-resident macrophages, independently of transendothelial glucose transport.
Lowering endothelial GLUT1 through genetic deletion or upon a short-term high-fat diet rewires endothelial glucose metabolism, thereby increasing angiocrine OPN secretion. This promotes resident macrophage accumulation and activation, which leads to muscle insulin resistance.
https://www.cell.com/cell-metabolism/fulltext/S1550-4131(24)00335-8