Dysregulation of deubiquitinylases in gastrointestinal diseases
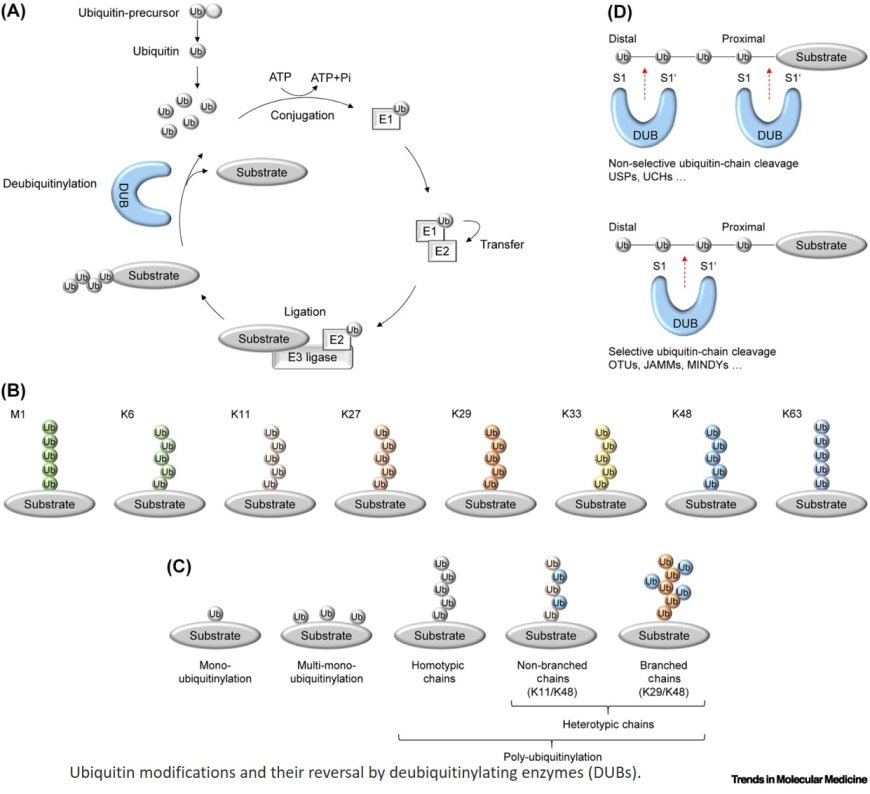
By reversing E3 ubiquitin ligase dependent ubiquitinylation, deubiquitinylating enzymes (DUBs) regulate a variety of cellular processes, such that their dysregulation through downregulation, upregulation, or mutation has adverse effects on gastrointestinal diseases, including cancer.
Infection by pathogens modulates DUB expression and activity, which supports persistent infection and influences the immune response and cell survival.
Transwell co-culture systems containing gastrointestinal organoids and other cells from the microenvironment are versatile tools for the analysis of DUB-dependent pathophysiology under near-in vivo conditions.
Therapeutic targeting of DUBs by inhibitors is an emerging field that also includes the evaluation of combination therapies with conventional chemotherapeutics and the development of new intervention strategies by proteolysis targeting chimeras (PROTACs) for DUB degradation.
https://www.cell.com/trends/molecular-medicine/fulltext/S1471-4914(25)00001-2
https://sciencemission.com/Dysregulation-of-deubiquitinylases