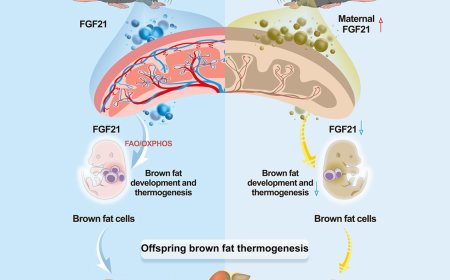
Endolysosomal dysfunction in Alzheimer’s disease from amyloid precursor protein carboxy-terminal fragments
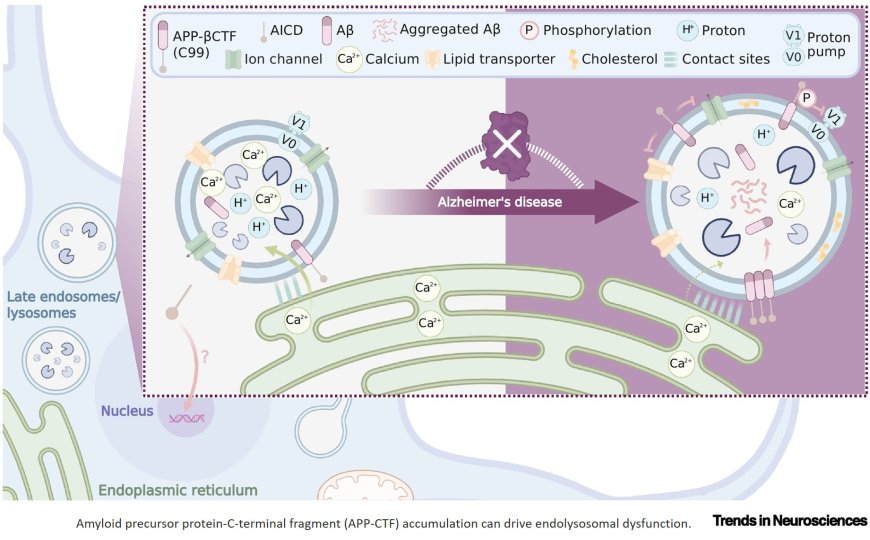
Emerging evidence identifies amyloid precursor protein C-terminal fragments (APP-CTFs) as critical mediators of neuronal dysfunction, independently from β-amyloid peptides.
γ-secretase-mediated intramembrane proteolysis may be required to abrogate APP function.
In the context of Alzheimer’s disease (AD), APP-CTFs may operate as a primary trigger by disrupting endolysosomal homeostasis.
Mechanistically, APP-CTFs accumulation at late endosomes/lysosomes– endoplasmic reticulum contacts impairs ion and lipid signaling. APP-CTF toxicity is underappreciated in advancing preventive therapeutic strategies in AD.
https://www.cell.com/trends/neurosciences/fulltext/S0166-2236(25)00102-X