General anesthesia activates a central anxiolytic center in the BNST
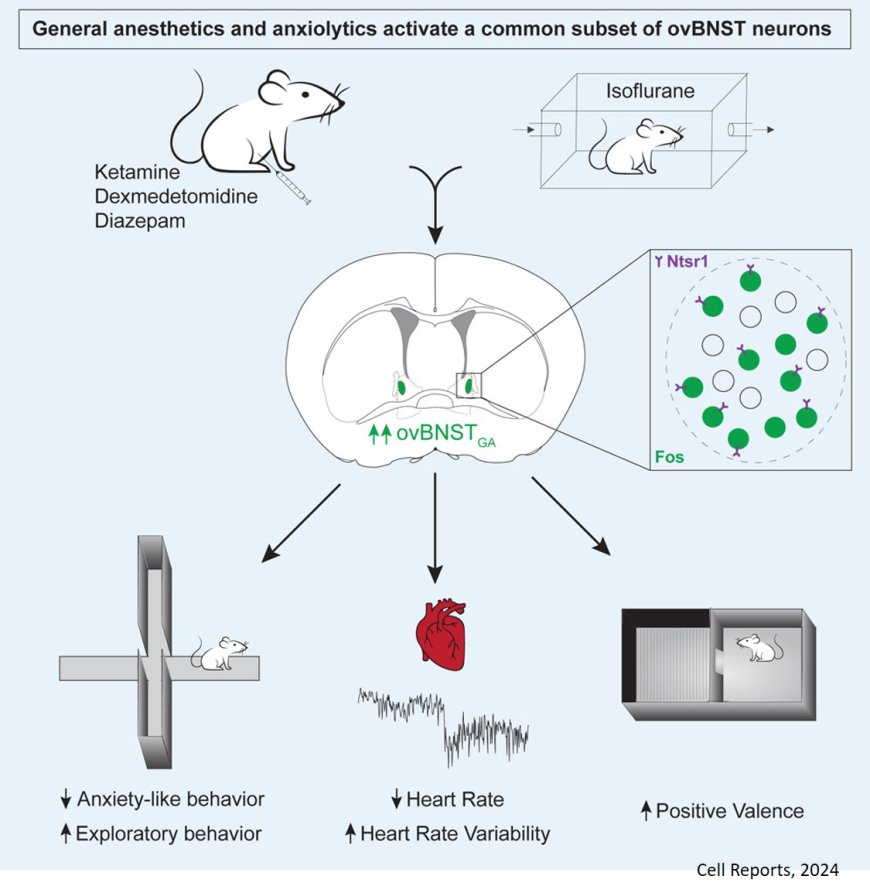
The anxiolytic mechanisms of general anesthetics is not clear yet.
In this article, the researchers characterize a population of neurons in the bed nucleus of the stria terminalis that is activated by general anesthetics and diazepam. They show that the majority of ovBNSTGA neurons express neurotensin receptor 1 (Ntsr1) and form circuits with brain regions known to regulate anxiety and stress responses.
Optogenetic activation of ovBNSTGA or ovBNSTNtsr1 neurons significantly attenuated anxiety-like behaviors in both naive animals and mice with inflammatory pain, while inhibition of these cells elevated anxiety. Activation of these neurons decreased heart rate and increased heart rate variability, suggesting that they reduce anxiety by modulating autonomic responses.
https://www.cell.com/cell-reports/fulltext/S2211-1247(24)01260-9
https://sciencemission.com/General-anesthesia-activates-a-central-anxiolytic-center-in-the-BNST