Genetic Risk in Alzheimer Disease
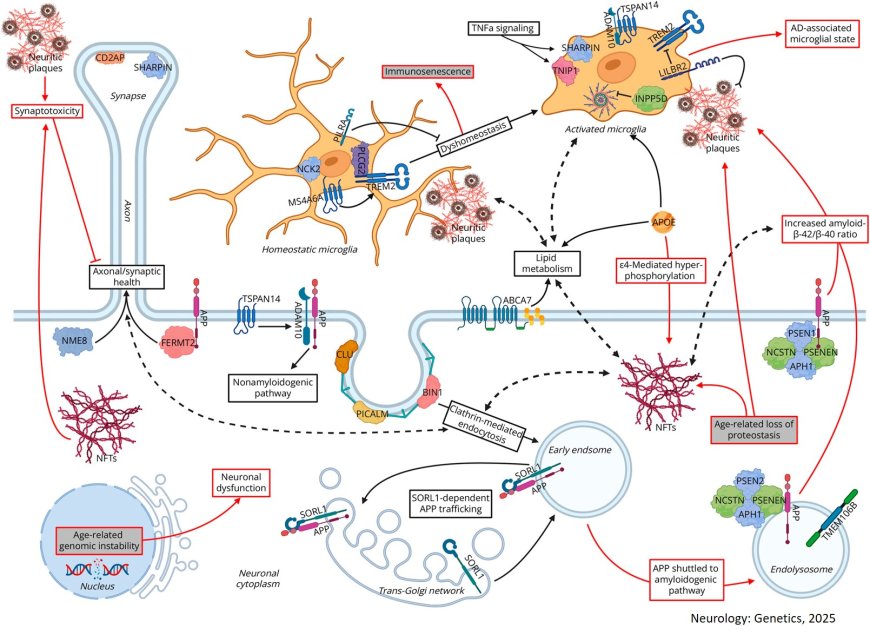
Amyloid-β and tau protein aggregates are hallmarks of Alzheimer disease (AD).
Various genetic mutations are also implicated in AD.
In this review, the authors discuss the discovery of familial autosomal dominant genes, the identification of candidate genes associated with AD, and genetic variants conferring higher risk of developing AD compared with the general population.
They also discuss important features of AD risk due to the APOE e4 allele.
The authors also discuss the genetic factors that may protect from AD.
The authors evaluate the limitations of information gleaned from genome-wide association studies in AD over the years and thus provide genetic complexity in understanding AD.
https://www.neurology.org/doi/10.1212/NXG.0000000000200224
https://sciencemission.com/Genetic-Risk-in-Alzheimer-Disease