Local protein synthesis at neuromuscular synapses is required for motor functions
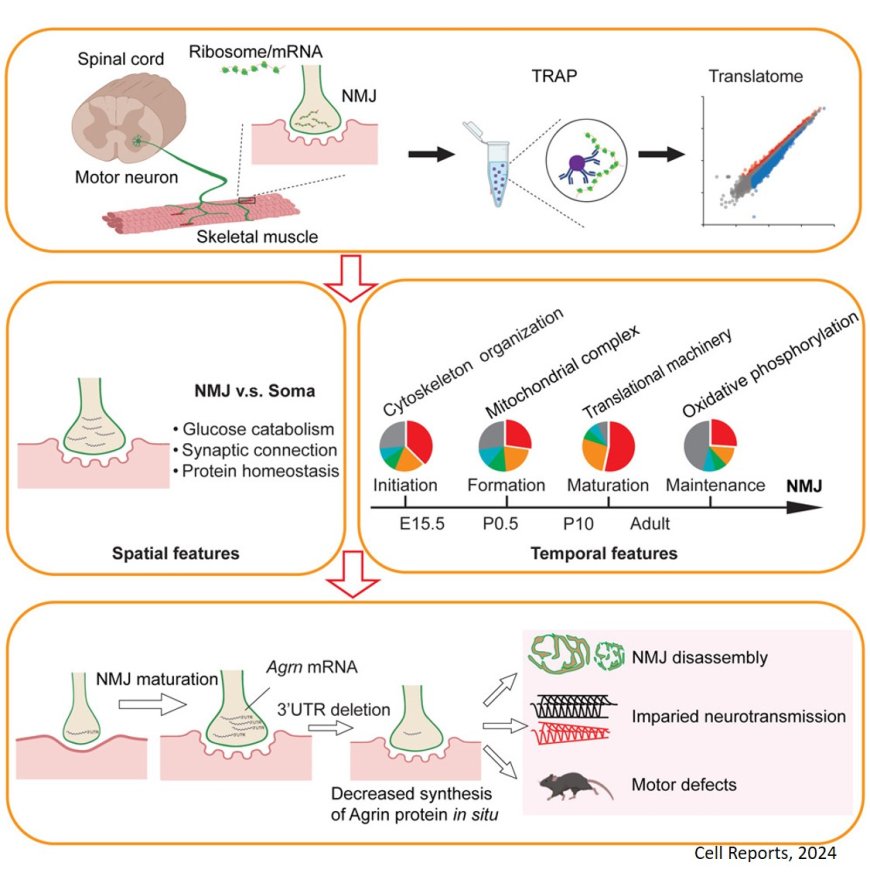
Motor neuron axons extend over great distances to control muscle contraction via neuromuscular junctions (NMJs). However, local translation at the NMJs in vivo has not been identified.
The researchers spatiotemporally profiled the mRNA translatome at NMJs. They found mRNAs associated with glucose catabolism, synaptic connection, and protein homeostasis are enriched at presynapses. Local translation at the synapse shifts from the assembly of cytoskeletal components during early developmental stages to energy production in adulthood.
The authors also identified that the key molecule for NMJ assembly, mRNA for Agrn. is present at synapses and locally translated to regulate motor functions in adults.
Disrupting the axonal location of Agrn mRNA causes impairment of synaptic transmission and motor functions in adult mice indicating the requirement of local translation for motor functions.
https://www.cell.com/cell-reports/fulltext/S2211-1247(24)01012-X