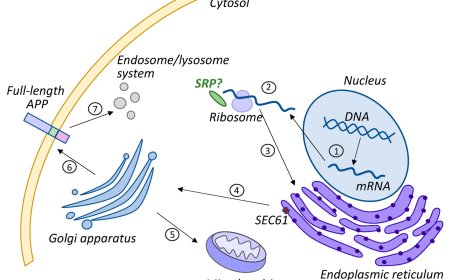
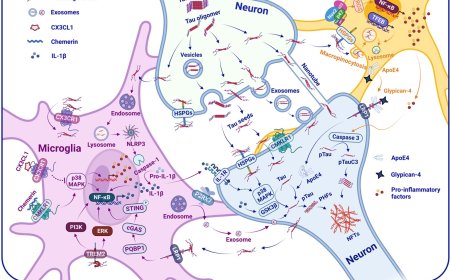
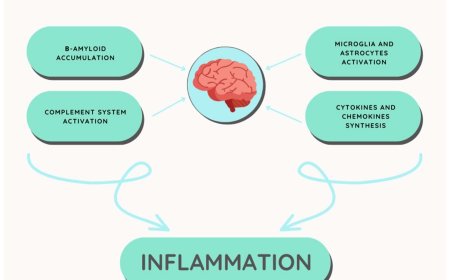
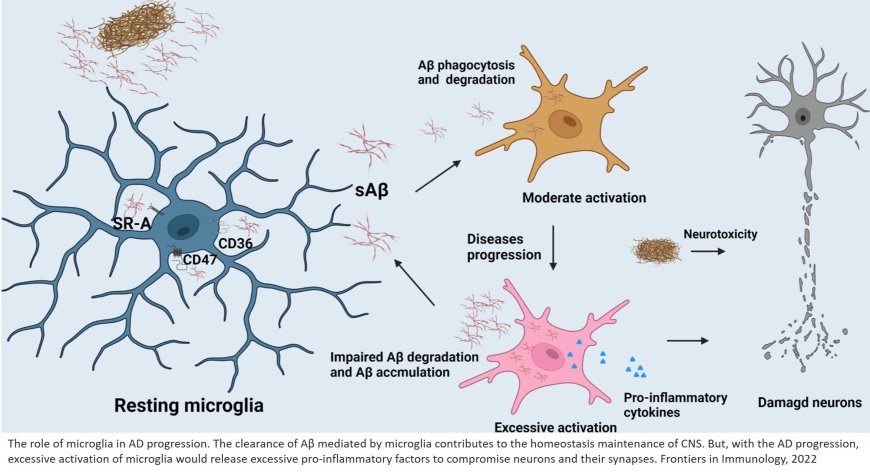
Microglia in Alzheimer’s disease
Microglia are a type of glial cell located throughout the brain and spinal cord. They act as the first and main form of active immune defense in the central nervous system. Microglia play a crucial role in Alzheimer's disease (AD), and their dysfunction has been implicated in the disease's pathogenesis.
Microglial Functions in Alzheimer's Disease
1. Phagocytosis and clearance: Microglia help remove amyloid-β (Aβ) plaques and other toxic substances from the brain.
2. Inflammatory responses: Microglia produce pro-inflammatory and anti-inflammatory cytokines, which influence the immune response and disease progression.
3. Neurotrophic support: Microglia produce neurotrophic factors, such as brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), which support neuronal health and survival.
4. Synaptic pruning and plasticity: Microglia help regulate synaptic connections and plasticity, which are critical for learning and memory.
Microglial Dysfunction in Alzheimer's Disease
1. Impaired phagocytosis: Microglia in AD brains show reduced phagocytic activity, leading to the accumulation of Aβ plaques.
2. Chronic inflammation: Microglia in AD brains produce excessive pro-inflammatory cytokines, contributing to chronic inflammation and neuronal damage.
3. Altered neurotrophic support: Microglia in AD brains show reduced production of neurotrophic factors, exacerbating neuronal vulnerability.
4. Dysregulated synaptic pruning: Microglia in AD brains may contribute to excessive synaptic pruning, leading to cognitive decline.
Therapeutic Targeting of Microglia in Alzheimer's Disease
1. Modulation of microglial activation: Targeting microglial activation states to reduce chronic inflammation and promote phagocytic activity.
2. Enhancement of phagocytic function: Developing therapies to improve microglial phagocytosis and clearance of Aβ plaques.
3. Neurotrophic support: Promoting microglial production of neurotrophic factors to support neuronal health and survival.
4. Synaptic modulation: Targeting microglial regulation of synaptic pruning and plasticity to prevent excessive synaptic loss.
Current Research Directions
1. Microglial heterogeneity: Investigating the diversity of microglial populations and their specific roles in AD.
2. Microglial-Neuronal Interactions: Elucidating the complex interactions between microglia and neurons in AD.
3. Microglial Targeting Therapies: Developing novel therapeutic strategies to modulate microglial function and promote disease-modifying effects in AD.
https://www.frontiersin.org/journals/immunology/articles/10.3389/fimmu.2022.856376/full
https://sciencemission.com/Microglia-in-Alzheimer%E2%80%99s-Disease