Neuroinflammation in Alzheimer’s disease
Neuroinflammation plays a significant role in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer's disease (AD). Here's an overview:
Neuroinflammatory Response in Alzheimer's Disease
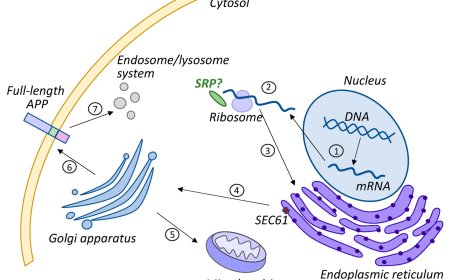
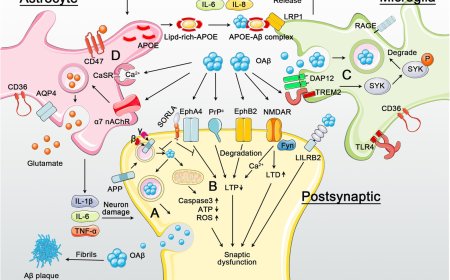
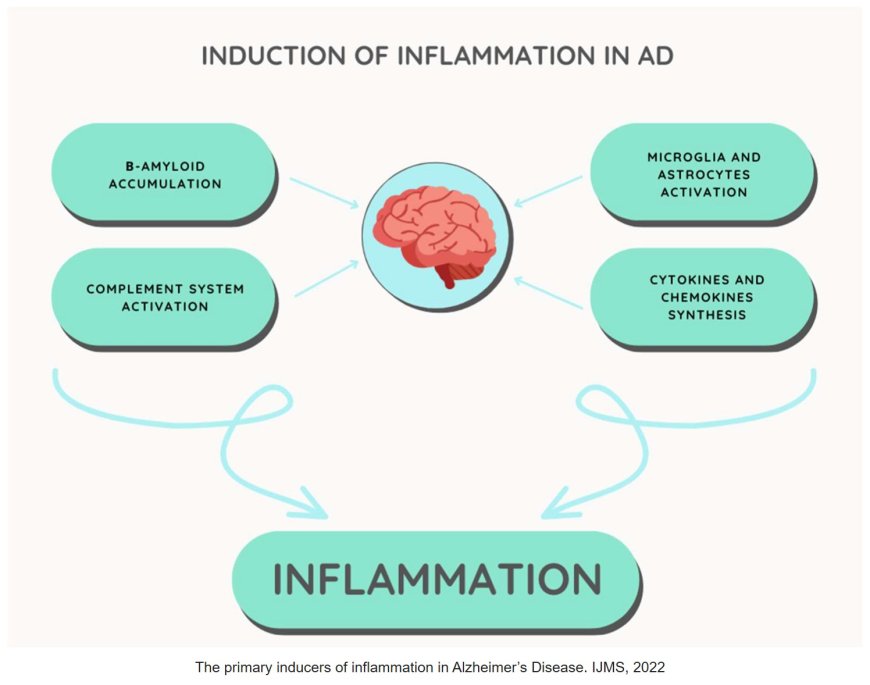
1. Activation of immune cells: Microglia, the brain's resident immune cells, are activated in response to amyloid-β (Aβ) plaques and other toxic substances.
2. Release of pro-inflammatory cytokines: Activated microglia release pro-inflammatory cytokines, such as TNF-α, IL-1β, and IL-6, which contribute to chronic inflammation.
3. Astrocyte activation: Astrocytes, another type of glial cell, are also activated and contribute to the inflammatory response.
Consequences of Neuroinflammation in Alzheimer's Disease
1. Neuronal damage and death: Chronic inflammation leads to the release of neurotoxic substances, which damage and kill neurons.
2. Disruption of the blood-brain barrier: Neuroinflammation can disrupt the blood-brain barrier, allowing toxins and immune cells to enter the brain.
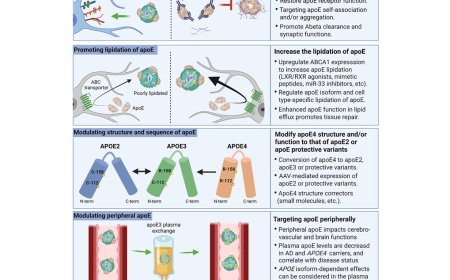
3. Promotion of amyloid-β accumulation: Neuroinflammation can promote the accumulation of Aβ plaques, which are a hallmark of AD.
Key Players in Neuroinflammation
1. Microglia: Microglia are the primary immune cells involved in neuroinflammation.
2. Astrocytes: Astrocytes contribute to the inflammatory response and can also produce anti-inflammatory cytokines.
3. T cells: T cells, a type of immune cell, can infiltrate the brain and contribute to neuroinflammation.
Therapeutic Strategies
1. Anti-inflammatory drugs: Anti-inflammatory drugs, such as NSAIDs, have been explored as potential therapeutic agents.
2. Immunomodulatory therapies: Immunomodulatory therapies, such as vaccines and antibodies, aim to modulate the immune response and reduce neuroinflammation.
3. Neuroprotective agents: Neuroprotective agents, such as antioxidants and neurotrophic factors, aim to protect neurons from damage caused by neuroinflammation.
Current Research Directions
1. Understanding the role of microglia: Research is focused on understanding the complex role of microglia in neuroinflammation and AD.
2. Identifying new therapeutic targets: Researchers are identifying new therapeutic targets, such as the NLRP3 inflammasome, to modulate neuroinflammation.
3. Developing personalized therapies: Personalized therapies, based on an individual's unique immune profile, are being explored to treat AD.
https://www.mdpi.com/1422-0067/24/7/6518
https://sciencemission.com/Inflammatory-Processes-in-Alzheimer%E2%80%99s-Disease