Microglial regulation of cortical remyelination
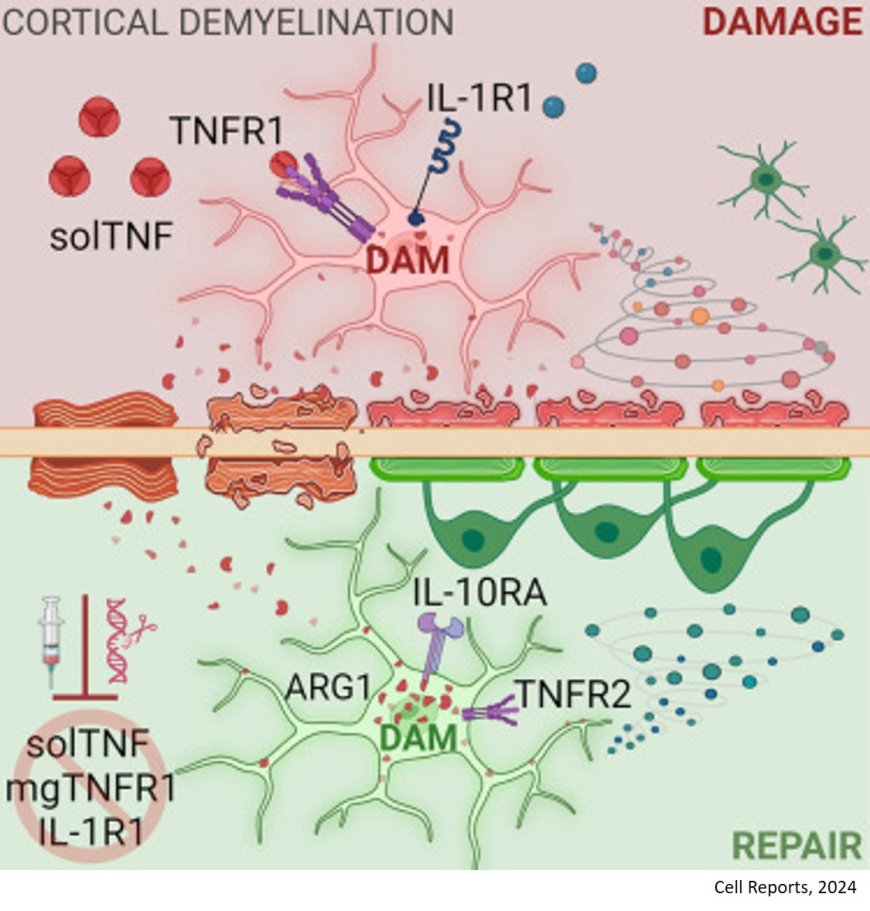
Mechanisms that control CNS remyelination are not clearly understood.
The researchers show that highly activated inflammatory microglia mediate remyelination in a cortical demyelination model. They identify microglia sensing of solTNF through TNFR1 as an immune checkpoint in the polarization between reparative and damaging microglia,
The authors show that microglia-specific deletion of tumor necrosis factor receptor 1 (TNFR1) and inhibition of soluble TNF (solTNF) or downstream interleukin-1 receptor (IL-1R) allow maturation of highly activated disease-associated microglia with increased size and myelin phagocytosis capacity that accelerate cortical remyelination and motor recovery.
The results reveal potential therapeutic targets for restoring myelin and slowing the progression of CNS demyelinating diseases.
https://www.cell.com/cell-reports/fulltext/S2211-1247(24)01245-2