Myeloperoxidase role in obesity
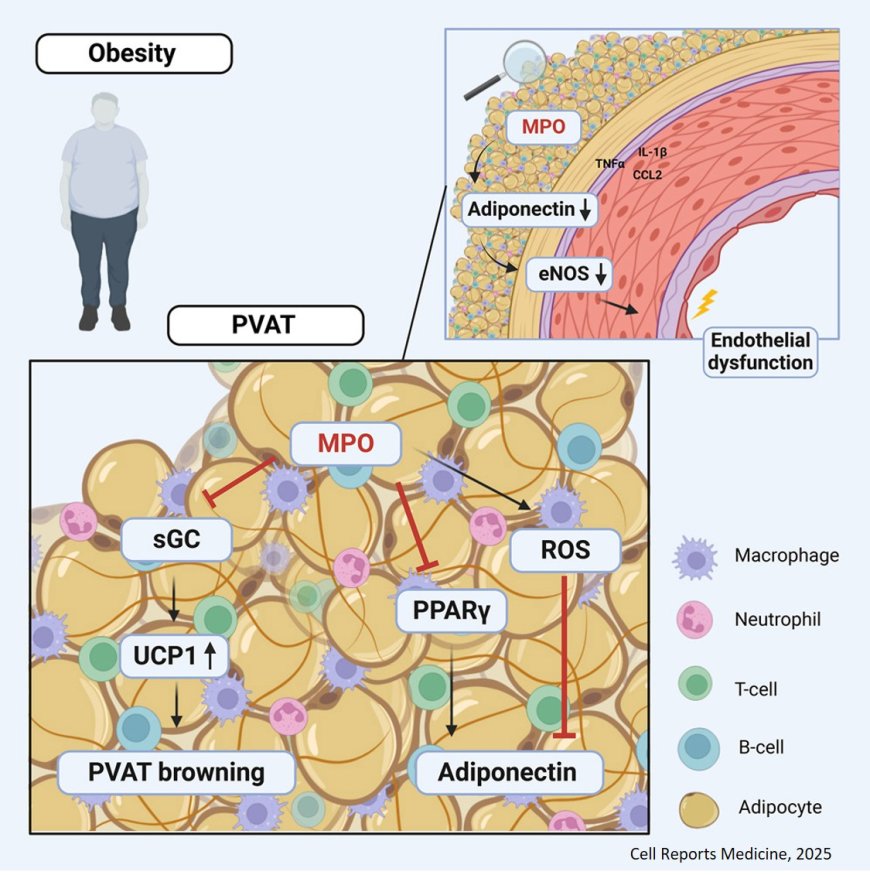
Endothelial dysfunction and inflammation in adipose tissue contribute to obesity.
The researchers show that myeloperoxidase (MPO) links obesity to vascular dysfunction by driving perivascular adipose tissue (PVAT) inflammation.
They show that MPO levels correlate with body weight and endothelial dysfunction in obesity patients.
MPO deficiency reduces PVAT inflammation, promotes adipocyte ‘‘beiging’’ via soluble guanylyl cyclase β1 (sGC-β1), increases adiponectin secretion, and improves vascular function.
Mechanistically, adiponectin (APN) secretion improves endothelial function and reduces arterial stiffness. In vitro, MPO-treated human white adipocytes show lower APN and brown adipocyte marker expression but increased inflammation.
https://www.cell.com/cell-reports-medicine/fulltext/S2666-3791(25)00160-0
https://sciencemission.com/Myeloperoxidase-impacts-vascular-function