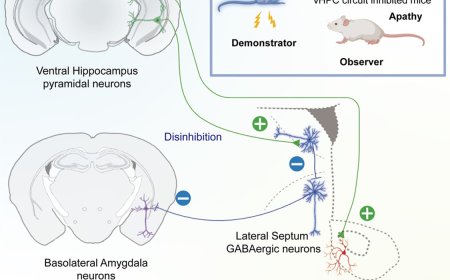
Photoperiod-driven clock function in plants
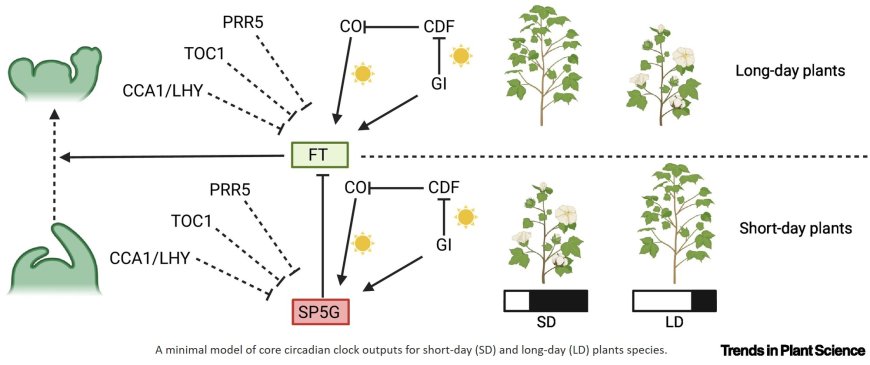
A minimalistic regulatory model integrating transcriptomes (RNA sequencing, qPCR, microarray) can account for developmental transition in both longday plants and short-day plants.
This opinion provides insights into how plants with opposing photoperiodic developmental transition responses could use a shared circadian clock regulatory core to drive developmental transition, with species-specific downstream modifications leading to diversification in developmental transition response to the photoperiod.
Comparative analysis suggests that diversification in circadian clock output genes could lead to opposite developmental transition responses to the photoperiod.
This unified model could bridge the gap in understanding the molecular basis of photoperiodic developmental transition across species with distant responses to the photoperiod.
https://www.cell.com/trends/plant-science/fulltext/S1360-1385(25)00012-3