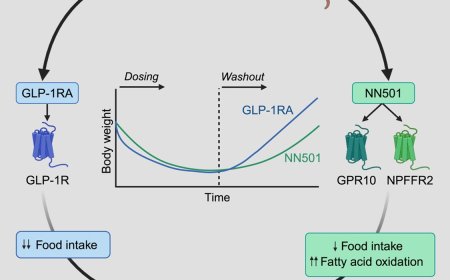
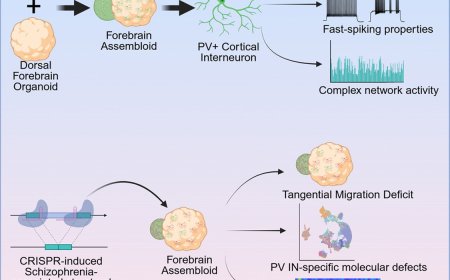
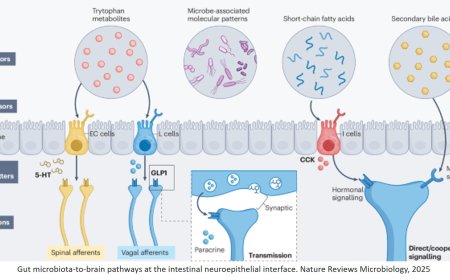
Pyruvate dehydrogenase and cocaine-associated memory

Drug addiction involves formation of drug-associated memory through neural activation. But, mechanisms underlying energy production for neuronal activation not known.
The researchers report that cocaine markedly increases the level of pyruvate dehydrogenase (PDH) complex E1 subunit α (PDHA1) crotonylation at the K39 residue in the dorsal dentate gyrus (dDG) through P300 catalysis.
Crotonylated PDHA1 promotes pyruvate metabolism by activating PDH to increase ATP production, thus providing energy for hippocampal neuronal activation and promoting cocaine-associated memory recall.
https://www.cell.com/cell-reports/fulltext/S2211-1247(24)00858-1