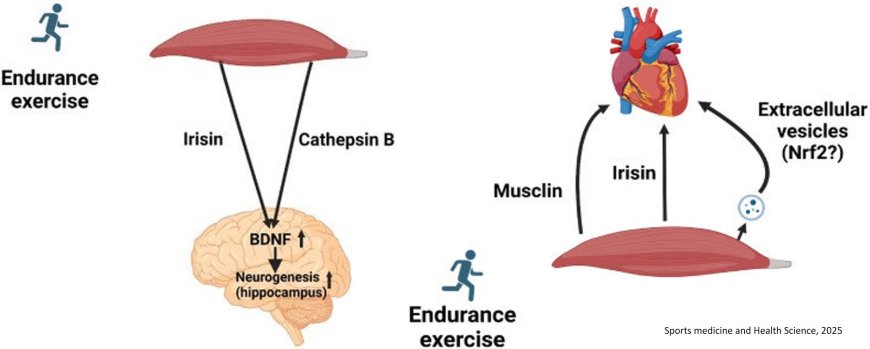
Skeletal muscle-heart, skeletal muscle-brain crosstalk during exercise
The current physical activity guidelines recommend that adults perform both aerobic and resistance exercise training to improve health and reduce the risk of all-cause mortality.
Abundant evidence indicates that meeting the current physical activity guidelines reduces the risk of all-cause mortality by reducing the risk of developing numerous chronic diseases (e.g., coronary heart disease, stroke, cancer, type 2 diabetes, etc).
Although the health benefits of exercise are established, the mechanisms responsible for physical activity-related health benefits remain a hot topic for research.
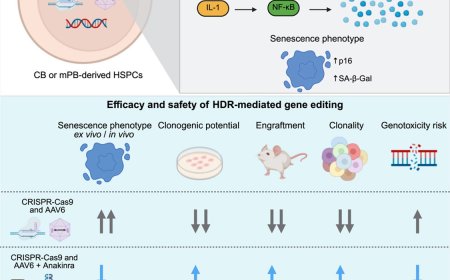
The search for the “exercise factors” responsible for physical activity-induced health benefits has led to the discovery of exerkines.
Exerkines are molecules released into the blood during exercise; these molecules include proteins, peptides, and nucleic acids that exert their effects on numerous tissues.
Myokines key players responsible for exercise-induced adaptations in multiple organs through muscle-organ crosstalk.
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2666337625000307
https://sciencemission.com/Health-benefits-of-physical-activity