TREM2 and sTREM2 in Alzheimer’s disease

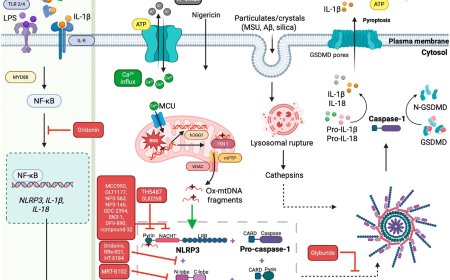
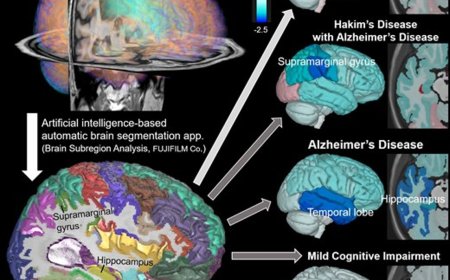
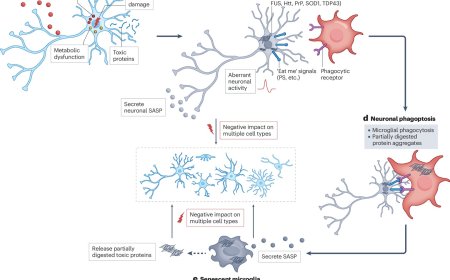
Brain microglia expresses triggering receptor expressed on myeloid cells 2 (TREM2), which play a crucial role in neurodegeneration. TREM2 triggers immune responses upon sensing pathological development and tissue damages.
TREM2 binds diverse ligands and activates downstream pathways that regulate microglial phagocytosis, inflammatory responses, and metabolic reprogramming.
TREM2 exists both in its membrane-bound form and as a soluble variant (sTREM2), that latter is generated through proteolytic shedding or alternative splicing and can be detected in cerebrospinal fluid and plasma.
This review provides a comprehensive overview of the molecular functions, regulatory mechanisms, and pathological implications of TREM2 and sTREM2 in AD.
The authors discuss their potential roles in diagnostics and therapeutics of AD.
https://molecularneurodegeneration.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s13024-025-00834-z
https://sciencemission.com/TREM2-and-sTREM2-in-Alzheimer’s-disease