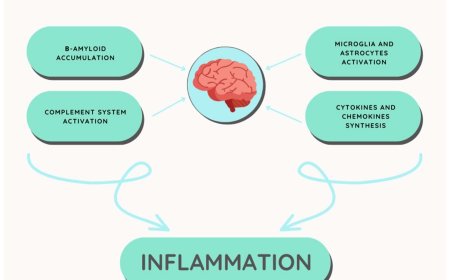
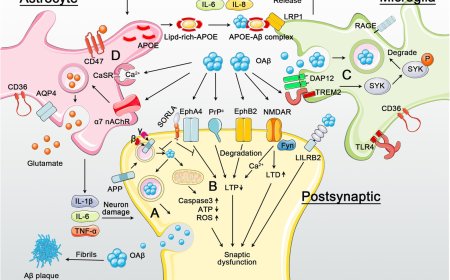
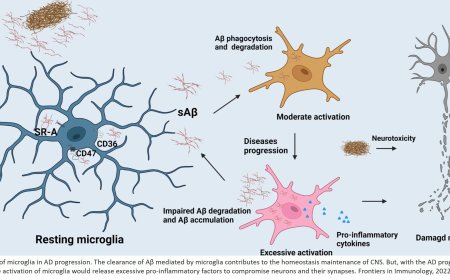
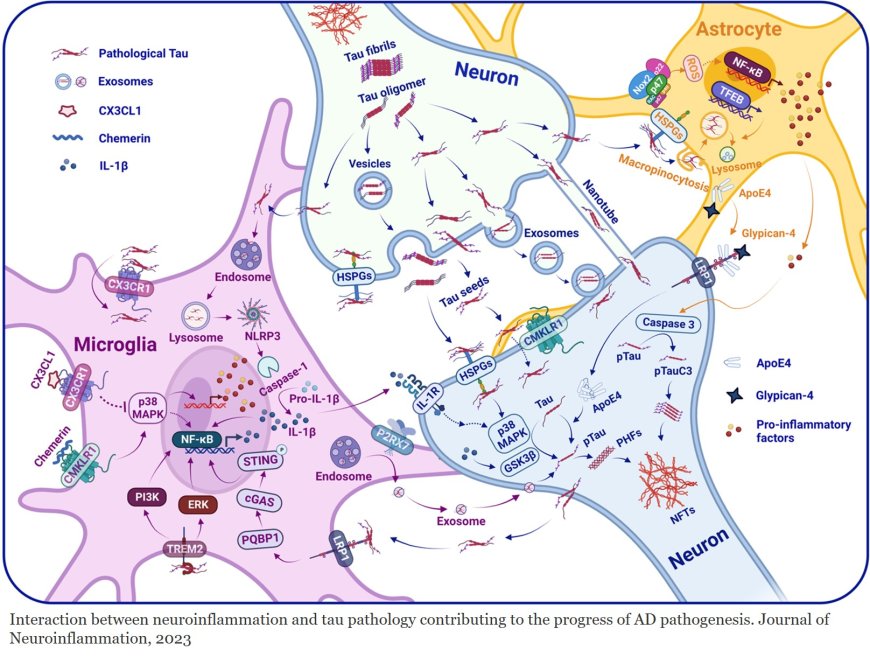
Tau in Alzheimer’s disease
Tau is a microtubule-associated protein that plays a crucial role in maintaining the structure and stability of microtubules in neurons. Here's an overview of tau biology and its involvement in disease:
Tau Biology
1. Structure: Tau is a soluble protein composed of 4-6 repeat domains, which bind to microtubules.
2. Function: Tau regulates microtubule dynamics, stability, and organization, essential for axonal transport, neuronal morphology, and synaptic plasticity.
3. Isoforms: Six tau isoforms exist, resulting from alternative splicing of the MAPT gene.
4. Phosphorylation: Tau is phosphorylated by various kinases, regulating its activity and microtubule binding.
Tau in Disease
1. Alzheimer's Disease: Tau is a hallmark of Alzheimer's disease, forming neurofibrillary tangles (NFTs) and neuropil threads.
2. Tauopathies: A group of neurodegenerative disorders characterized by tau pathology, including:
- Frontotemporal dementia (FTD)
- Progressive supranuclear palsy (PSP)
- Corticobasal degeneration (CBD)
- Chronic traumatic encephalopathy (CTE)
3. Tau aggregation: Tau misfolding and aggregation lead to the formation of toxic species, contributing to neuronal damage and disease progression.
4. Tau propagation: Tau pathology can spread between neurons, contributing to disease progression and neurodegeneration.
Therapeutic Targets
1. Tau aggregation inhibitors: Compounds targeting tau aggregation, such as methylene blue and TRx0237.
2. Tau phosphorylation modulators: Agents regulating tau phosphorylation, like kinase inhibitors and phosphatase activators.
3. Tau immunotherapy: Immunotherapies targeting tau, including vaccines and antibodies.
4. Microtubule stabilizers: Compounds stabilizing microtubules, reducing tau-mediated toxicity.
2. Biomarkers: Developing reliable biomarkers for tau pathology and disease progression.
3. Therapeutic efficacy: Demonstrating the efficacy of tau-targeting therapies in clinical trials.
4. Combination therapies: Exploring combination therapies targeting multiple aspects of tau biology and disease pathology.
https://jneuroinflammation.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s12974-023-02853-3
https://sciencemission.com/Tau-and-neuroinfammation-in-Alzheimer%E2%80%99s