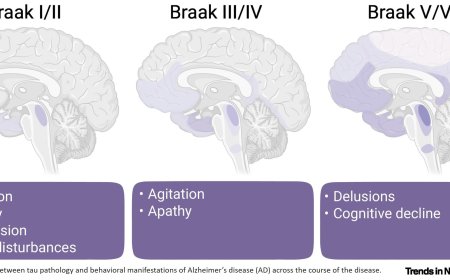
Elevated calneuron-1 induces schizophrenia-like deficits
Calneuron-1 gene has been linked to schizophrenia but the mechanism is not well understood
The researchers report in this study that the schizophrenia-risk gene calneuron-1 is elevated in dorsolateral prefrontal cortex of schizophrenia patients, and elicits schizophrenia-like behavior, and impairs network communication in mice.
Overexpression of Calneuron-1 in the medial prefrontal cortex (mPFC) of mice elicited SCZ-related behavioral disabilities, with disrupted rhythmogenesis within the mPFC, impaired functional connectivity between the hippocampus and the mPFC.
Calneuron-1 is an accessory subunit of muscarinic M1R that inhibits G-protein coupling and shuts off M1R signaling in schizophrenia. The authors show that Calneuron-1 displaces Gαq11 from the third intracellular loop of M1R at elevated [Ca2+]i, thereby disrupting downstream signaling.
The M1R agonist xanomeline interrupts calneuron-1/M1R interaction and rescues schizophrenia related deficits.