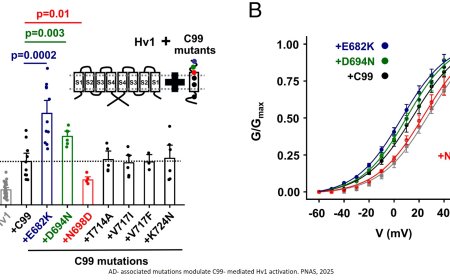
Cell vulnerability 'fingerprint' related to Parkinson's identified!
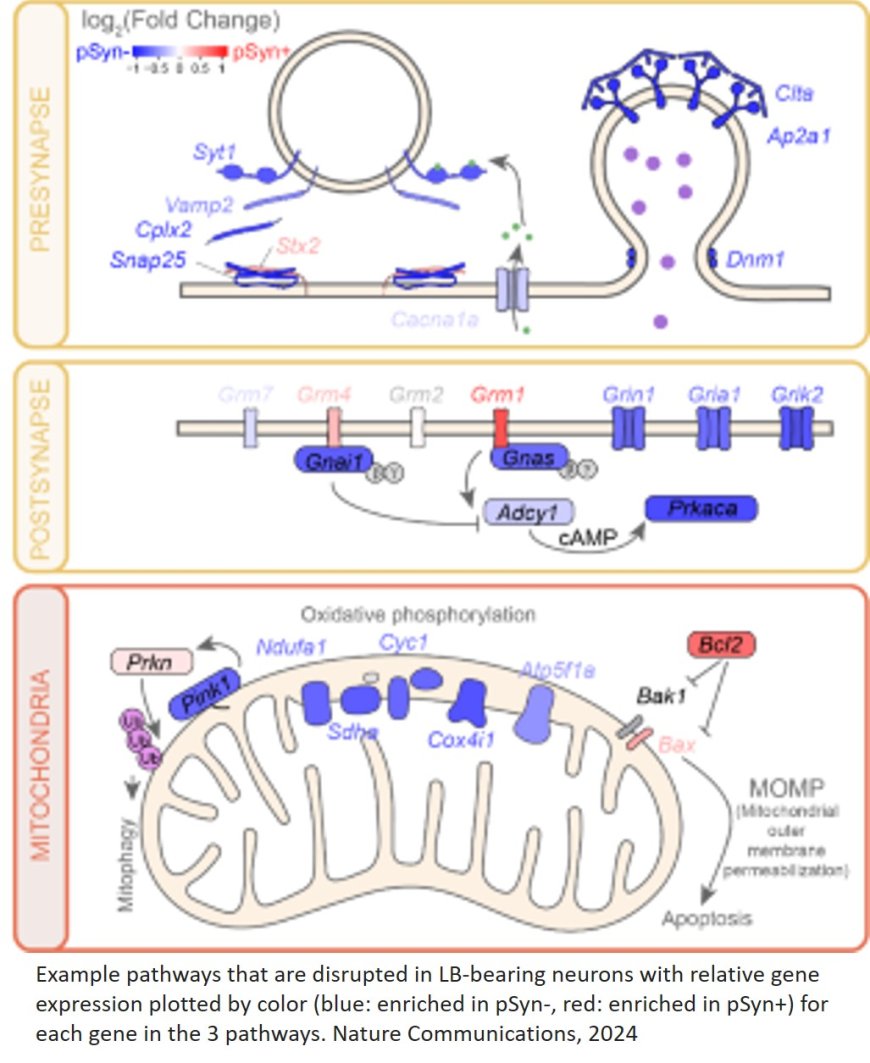
A new study offers a first look into the complex molecular changes that occur in brain cells with Lewy bodies, which are key pathological hallmarks of Parkinson’s disease and some dementias.
The findings, published in the journal Nature Communications, reveal that brain cells with Lewy bodies exhibit a specific gene expression pattern akin to a disease-related fingerprint.
“We’ve long known that Lewy bodies play a role in Parkinson’s and other neurodegenerative diseases but there are still many unanswered questions. Why are some cells more susceptible to Lewy bodies than others? How do Lewy bodies actually affect cells?” said the study’s corresponding author. “Our findings are an important starting point for better understanding how cells respond to Lewy bodies, which is an area of great potential for informing new therapies.
Lewy bodies are clumps of misshapen proteins that are believed to disrupt healthy cellular function and contribute to cell death in neurodegenerative disorders such as Parkinson’s and Lewy body dementia. Loss of these vital cells contributes to disease symptoms.
Thanks to recent technological advances, in particular a new technique called spatial transcriptomics, the team were able to compare brain cells with Lewy bodies to brain cells without Lewy bodies in deep detail. The pattern they identified includes genes that affect many critical processes required for brain health, including cellular communication, energy regulation, cellular trash removal, and inflammation. The study included preclinical models and cells from people with Parkinson’s.
“Our findings support the idea that cells with Lewy bodies affect other cells and processes in the brain,” the author said. “Moving forward, we plan to explore the molecular pathways disrupted by Lewy bodies to identify mechanisms that may be protective.”