Design to deployment of chimeric signaling proteins for microbial whole-cell biosensors
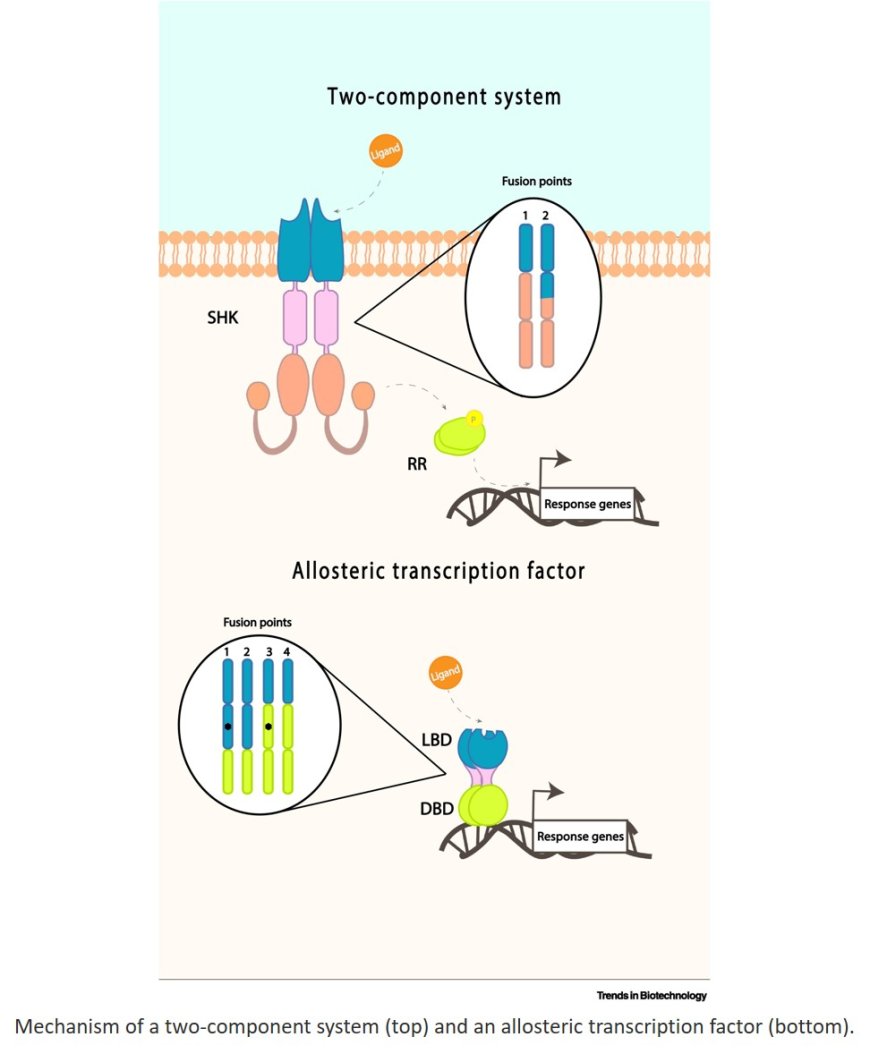
Chimeric signaling proteins are gaining traction in the development of microbial whole-cell biosensors (MWCBs), because they enable versatile combinations of input and output domains from various organisms.
Two-component systems and allosteric transcription factors are the most widely used architectures for developing responsive sensing elements in MWCBs.
Advances in domain swapping and chimeric fusion strategies are expanding MWCB capabilities, enabling detection of previously inaccessible or complex analytes.
Deployment of MWCBs in real-world settings requires advances in device integration, multiplexing, signal robustness, stability, and performance in context specific and variable conditions.
Despite promising field-ready prototypes, implementation remains limited by biological complexity, technical constraints, regulatory ambiguity, and inconsistent terminology, among others.
https://www.cell.com/trends/biotechnology/fulltext/S0167-7799(25)00320-8













