Role of clusterin (CLU) in Alzheimer’s disease
Clusterin (CLU) has been implicated in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s disease (AD), but the molecular mechanism is not well understood.
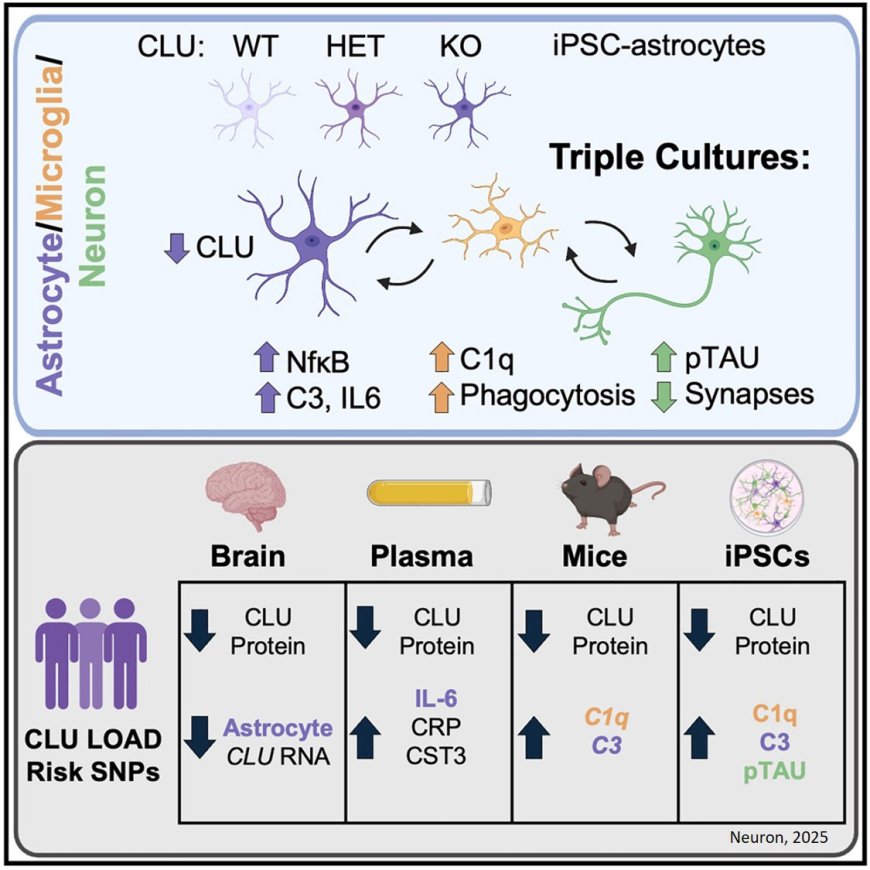
The authors show increased nuclear factor κB (NF-κB)-dependent signaling and complement C3 secretion in CLU-deficient astrocytes. Reduction of astrocyte CLU also induced microglia-dependent modulation of extracellular apolipoprotein E (APOE) and phosphorylated tau, as well as increased microglial phagocytosis and reduced synapse numbers.
They also demonstrate that CLU AD-risk alleles are associated with reduced CLU protein and heightened inflammatory profiles.
The researchers reveal that AD-protective CLU alleles enhance CLU upregulation in response to accumulated neuropathology, thereby dampening inflammatory signaling between microglia and astrocytes.
Using several complementary approaches, they show that CLU upregulation in astrocytes protects neurons from microglia mediated induction of phospho-tau and synapse loss.
https://www.cell.com/neuron/fulltext/S0896-6273(25)00254-5
https://sciencemission.com/CLU-alleviates-Alzheimer%E2%80%99s-disease