Combination therapy to treat glioma
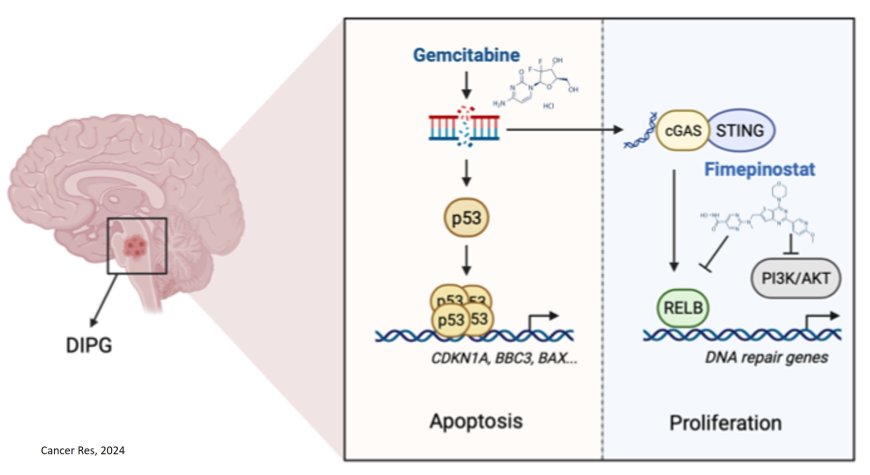
Diffuse intrinsic pontine glioma (DIPG) is the most aggressive pediatric brainstem tumor with a median survival of less than 12 months; seeking effective therapy is still the focus of the field.
Nearly 80% DIPG cells harbor H3K27M mutations, which caused global reduction in H3K27me3 levels, and H3K27M are considered as driver mutations for DIPG.
This understanding has recently inspired substantial efforts to develop drugs for treating DIPG based on global modulation of the histone methylation/acetylation balance. Whilst promising, the findings from such studies have had limited translational impacts. Hence, screening drugs for treating DIPG is highly demanding.
In addition to the characteristic H3K27M mutations, up to 90% of H3.3K27M mutant DIPG harbor alterations in the p53 pathway, including mutations in TP53 (accounting for 65~69%) itself, as well as protein phosphatase, Mg2+/Mn2+-dependent 1D (PPM1D, accounting for 20%~28%).
PPM1D truncating mutations promoted tumor progression in DIPG by destabilizing and inactivating p53. These evidences suggest that reactivating p53 tumor suppressive function in H3.3K27M DIPG cells might be a solution for DIPG therapy.
In this study, they used treatment-naïve patient-derived DIPG cell line and performed epigenetic compounds screening to identify that gemcitabine as a candidate.
As a pyrimidine analog, gemcitabine stabilized and activated p53, including increasing chromatin accessibility for p53 at apoptosis-related loci. Notably, the H3.3K27M mutation facilitates gemcitabine-induced apoptosis in DIPG. However, gemcitabine induced the transcription of ERV (endogenous retrovirus), which might activate cGAS-STING signaling, and stimulated non-canonical NFκB signaling.
A drug screen in gemcitabine-treated DIPG cells revealed that fimepinostat, a dual inhibitor of HDAC and PI3K, effectively suppressed the gemcitabine-induced NFκB signaling in addition to blocking PI3K/AKT activation.
Combination therapy comprising gemcitabine and fimepinostat elicited synergistic anti-tumor effects in vitro and in orthotopic H3.3K27M DIPG xenograft models.