Modified apelin inhibits colorectal cancer
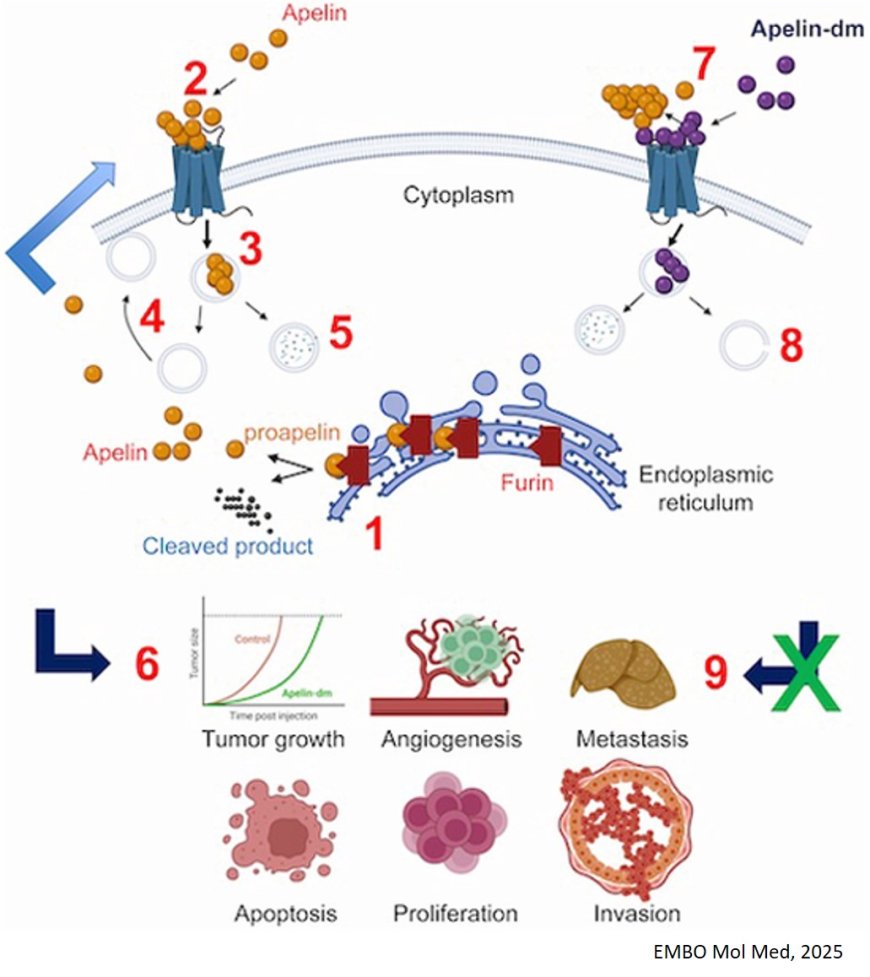
Apelin, an adipokine involved in tumor progression and metastasis, is cleaved from its precursor into the mature form by the proprotein convertase furin.
Apelin-dm, a modified variant of apelin created by altering proapelin cleavage sites, inhibits tumor growth, induces cell death, suppresses angiogenesis, and delays early colorectal liver metastasis events.
Proteomic analysis reveals a reciprocal regulatory relationship between apelin and apelin-dm, impacting proteins associated with clinical outcomes in colon cancer patients.
Apelin-dm modulates apelin receptor behavior, affecting receptor affinity, internalization, and repression of apelin signaling, influencing protein kinase activity.
Pharmacokinetic assessments confirm that apelin-dm is specific, stable, and undergoes efficient hepatic metabolism, with no significant toxicity.
https://www.embopress.org/doi/full/10.1038/s44321-025-00196-5
https://sciencemission.com/antimetastatic-strategy-in-colorectal-cancer