Protein lactylation in cancer
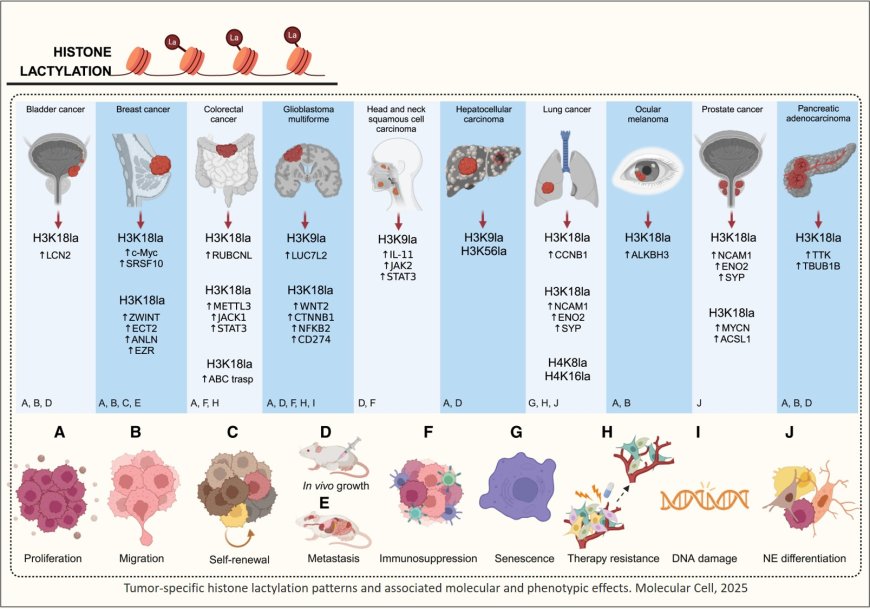
Lysine lactylation is a post-translational modification initially identified on histones but found to be present on non-histone proteins, and plays a pivotal role in transcriptional activation, protein function, and cellular processes like epigenetics and cancer biology.
Two major sources of the lactyl moiety have been currently distinguished: L-lactyl-CoA (precursor of the L-lactyl moiety) and S-D-lactylglutathione (precursor of the D-lactyl moiety), which enable enzymatic and non-enzymatic mechanisms of lysine lactylation, respectively. Acetyltransferases and deacetylases have been proposed as crucial mediators of lysine lactylation.
Lactylation exerts significant influence on critical cancer-related pathways, thereby shaping cellular behavior during malignant transformation and the metastatic cascade and targeting this modification is emerging as a significant opportunity for cancer treatment.
https://www.cell.com/molecular-cell/fulltext/S1097-2765(25)00142-X