Light physical activity shows great promise in reversing childhood obesity caused by being sedentary
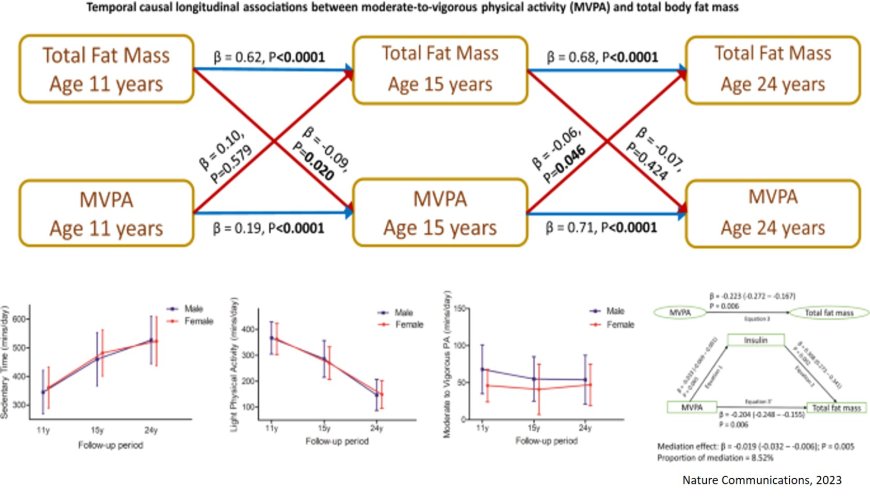
Increased sedentary time from childhood through young adulthood caused increased body fat and abdominal fat in a new follow-up study. However, the results also showed that light physical activity (LPA) may completely reverse the adverse process. Moderate-to-vigorous physical activity (MVPA) may only reduce the effect. The study was published in the prestigious Nature Communications.
Childhood and adolescent obesity have been associated with cardiovascular, metabolic, neurological, and musculoskeletal diseases in adulthood. Moreover, childhood obesity measured with body mass index was recently associated with an increased risk of premature death by the mid-forties. Body mass index (BMI) is a poor measure of obesity in childhood and adolescence since it does not distinguish between muscle mass and fat mass. Lifestyle changes such as reducing sedentary behavior and physical inactivity may improve health but long-term accelerometer data with gold-standard fat mass measures in children are scarce.
There is no information on the effectiveness of LPA in preventing obesity and how much sedentary time needs to be reduced for better health in the young population. These gaps in knowledge significantly limit current health guidelines. Recent reports concluded that more than 80% of adolescents across the globe do not meet the World Health Organization’s recommended average of 60 minutes/day of MVPA. It is estimated that physical inactivity will have caused 500 million new cases of heart disease, obesity, diabetes or other noncommunicable diseases by 2030, costing US$ 27 billion annually. This alarming forecast regarding the morbid danger of physical inactivity necessitates urgent research on the most effective preventive approach.
The long-term effect of movement behavior, objectively measured with an accelerometer, on dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry (DEXA)-measured total body fat mass and abdominal fat mass in the paediatric population has not been previously studied. This is due to the cost and logistic challenges of repeatedly measuring both movement behavior and fat mass in a very large cohort during growth from childhood through young adulthood.
The current study is the largest and the longest follow-up objectively measured PA and fat mass study in the world which used the University of Bristol’s Children of the 90s data (also known as the Avon Longitudinal Study of Parents and Children). The study included 6,059 children (53% females) aged 11 years who were followed up until age 24 years, with a follow-up time of approximately 13 years. Waist-worn accelerometer measures of sedentary time, LPA, and MVPA, and DEXA-measured fat mass and skeletal muscle mass were collected at ages 11, 15, and 24 years. These children also had their fasting blood samples repeatedly measured for, e.g., glucose, insulin, high-density lipoprotein cholesterol, low-density lipoprotein cholesterol, triglyceride, and high-sensitivity C-reactive protein. In addition, blood pressure, heart rate, smoking status, socio-economic status, and family history of cardiovascular disease were measured and controlled for in the analyses.
During the 13-year follow-up, sedentary time increased from approximately 6 hours/day in childhood to 9 hours/day in young adulthood. LPA decreased from 6 hours/day to 3 hours/day while MVPA was relatively stable around 50 mins/day from childhood through young adulthood. It was observed that each 1-minute spent sedentary was associated with a 1.3-gram increase in total body fat mass. Both male and female children gained an average of 10 kg of fat mass during growth from childhood until young adulthood. However, sedentary time potentially contributed 700 grams to 1 kg of fat mass (approximately 7 – 10%) of the total fat mass gained during growth from childhood until young adulthood.
Contrariwise, each 1-minute spent in LPA during growth from childhood through young adulthood was associated with a 3.6-gram reduction in total body fat mass. This implies that cumulative LPA decreased total body fat mass by 950 grams to 1.5 kg during growth from childhood to young adulthood, (approximately 9.5 – 15% decrease in overall gain in fat mass during the 13-year observation period). Of note, time spent in MVPA including meeting the 60-minute/day of MVPA recommended by the WHO during growth from childhood through young adulthood was associated with 70 to 170 grams (approximately 0.7 – 1.7%) reduction in total body fat mass.
“Our study provides novel information that would be useful in updating future health guidelines and policy statements. Prior to this study, it has not been possible to quantify the long-term contribution of sedentary time to fat mass obesity and the magnitude by which PA may reduce it. Our study confirmed the report from a recent meta-analysis of 140 school-based randomised controlled trials across the globe that engaging in MVPA had minimal or no effect in reducing childhood BMI-obesity,” say