Role of m6 A in RNA coding sequence
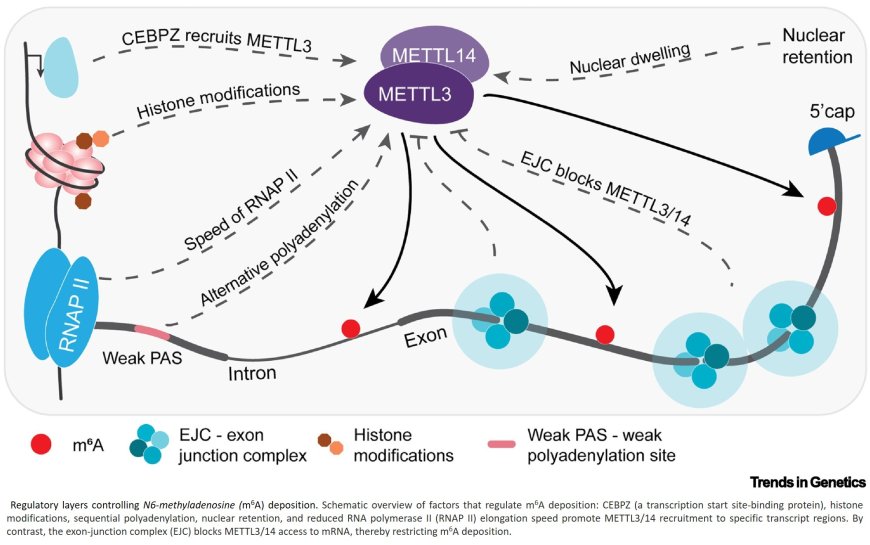
mRNA’s most abundant internal modification, N6-methyladenosine (m6A), plays a crucial role in regulating mRNA turnover.
The exon-junction complex (EJC) restricts METTL3 activity in the coding sequence (CDS), and thereby shapes the N6-methyladenosine (m6 A) landscape.
CDS m6 A modifications trigger rapid, translation-dependent mRNA degradation via CDS–m6A decay (CMD). Target transcripts for CMD are enriched in processing bodies (P-bodies).
The intricate link between m6 A deposition, translation, and decay enables efficient gene expression regulation.
CMD modulates the expression of physiologically relevant genes in healthy conditions and in disease, particularly in cancer.
https://www.cell.com/trends/genetics/fulltext/S0168-9525(25)00132-5