How maternal phthalates exposure leads to neurodevelopmental defects
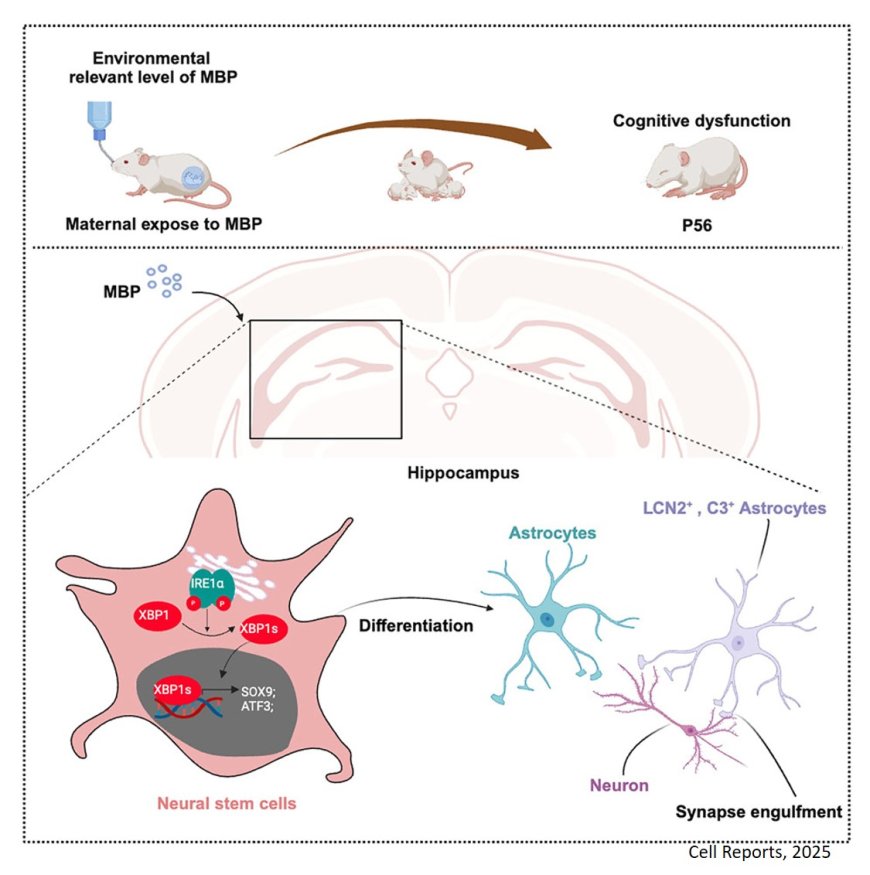
Chemical plasticizer, phthalate and its metabolite monobutyl phthalate (MBP) exposure to humans and especially to would-be moms may cause neurodevelopmental defects in the offsprings but the mechanism is unclear.
The researchers reveal that maternal exposure to MBP enhances neural stem cell differentiation into reactive astrocytes via the IRE1a/XBP1s pathway, leading to increased synapse phagocytosis and cognitive dysfunction in offspring.
The authors also demonstrate that conditional knockout or pharmacological inhibition of IRE1α markedly inhibits NSC differentiation into astrocytes and astrocyte reactivity, attenuates synapse phagocytosis, and improves cognitive function.
These findings highlight a molecular mechanism linking environmental phthalate exposure to neurodevelopmental defects.
https://www.cell.com/cell-reports/fulltext/S2211-1247(24)01477-3