Airway sensory neuronal reprogramming by cytokines in asthma
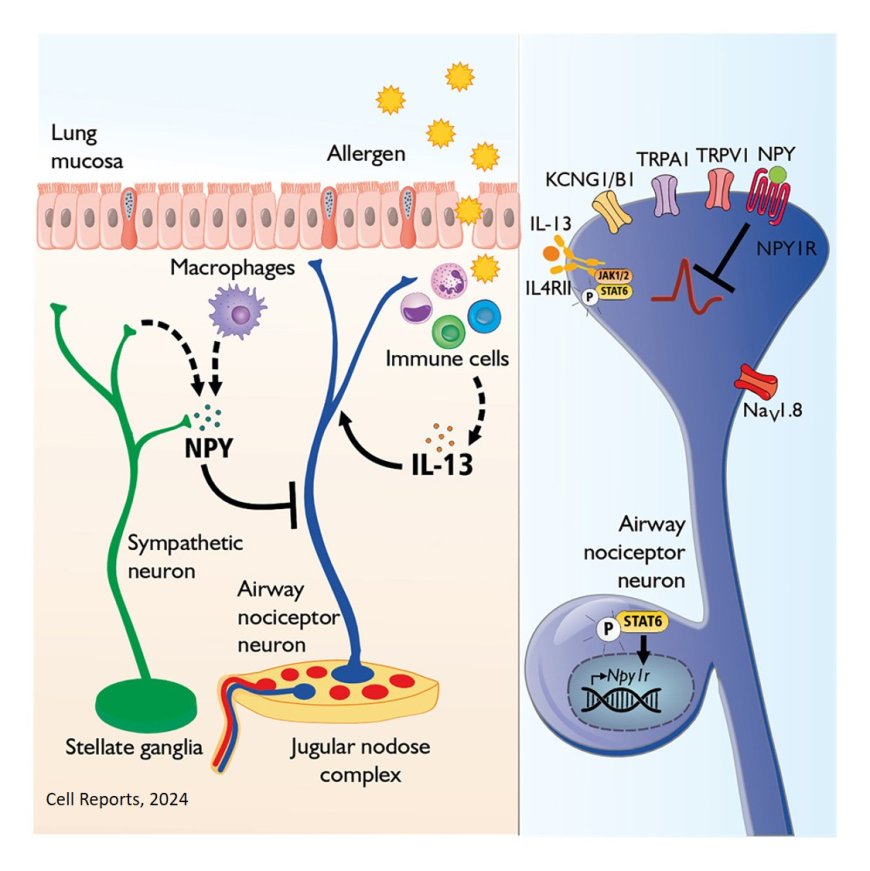
=Nociceptor neurons play multiple roles in asthma by exacerbating inflammation and bronchial hypersensitivity and triggering mucus metaplasia but the mechanisms are not known.
The researchers characterize a distinct subset of NPY1R-expressing sensory neurons that innervate the lung and describe their transcriptional and functional reprogramming. They show that interleukin 1β (IL-1β), IL-13, and brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) drive part of this reprogramming. IL-13 triggers Npy1r overexpression in nociceptors via the JAK/STAT6 pathway.
In parallel, NPY is released into the bronchoalveolar fluid of asthmatic mice, which limits the excitability of nociceptor neurons. Cell-specific knockout of NPY1R in nociceptor neurons in asthmatic mice altered T cell infiltration. Opposite findings are observed in asthmatic mice in which nociceptor neurons are chemically ablated.
Together, allergic airway inflammation reprograms airway nociceptor neurons to acquire a pro-inflammatory phenotype, while a compensatory mechanism involving NPY1R limits the activity of nociceptor neurons.
https://www.cell.com/cell-reports/fulltext/S2211-1247(24)01396-2
https://sciencemission.com/Cytokines-reprogram-airway-sensory-neurons-in-asthma