Ameliorating human aging and disease using methionine restriction and mimetics
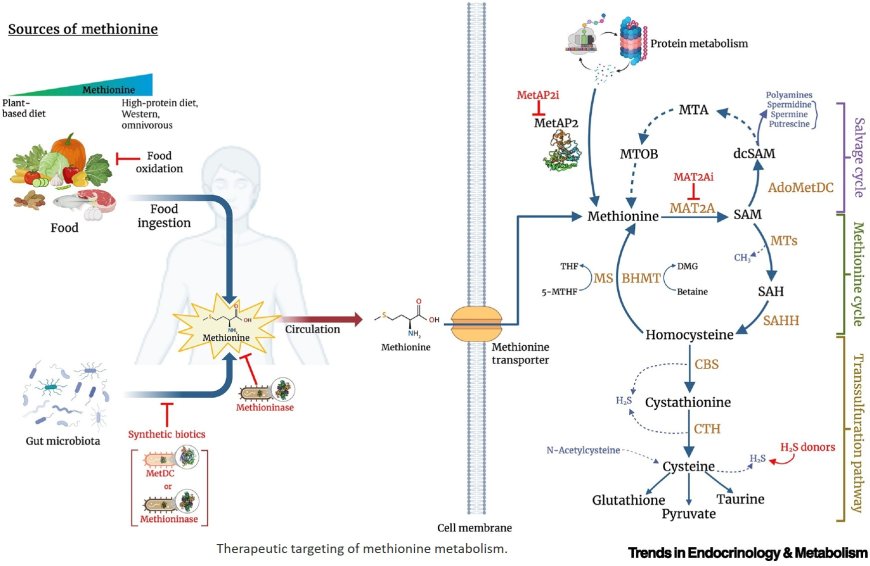
Methionine restriction (MetR) confers diverse benefits for health and disease in rodent models and prolongs lifespan across different species.
High levels of circulating methionine and related metabolites are risk factors for cardiovascular disease, dementia, osteoporotic fracture, and other age-related pathologies.
Implementing MetR in humans is challenging due to the low palatability of synthetic MetR diets and unfavorable side effects associated with continuous MetR.
Emerging alternatives to achieve MetR and/or MetR-like benefits include novel small molecules, synthetic biotics, and xenotopic tools, some of which are already in early-stage human clinical trials.
Mechanisms that may limit the efficacy of MetR in humans include microbiota-derived methionine, compensatory effects of cysteine, and intercellular methionine transfer.
https://www.cell.com/trends/endocrinology-metabolism/fulltext/S1043-2760(25)00198-5
https://sciencemission.com/Methionine-restriction-and-mimetics