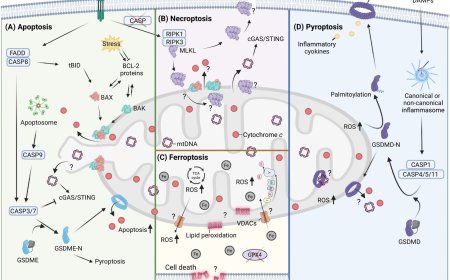
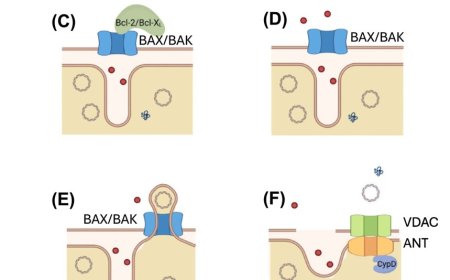
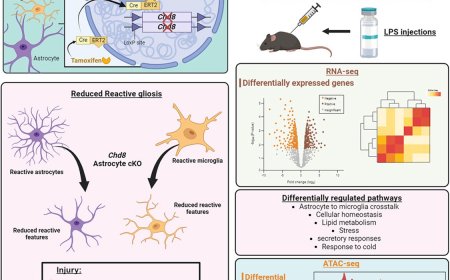
Astrocyte-to-neuron H2O2 signalling in long term memory formation

The role of reactive oxygen species (ROS) in memory formation is not known.
The researchers show that, in Drosophila, astrocytes signal to neurons with hydrogen peroxide to encode memories.
Mechanistically, stimulation of astrocytes by acetylcholine induces an increase in intracellular calcium ions, which triggers the generation of extracellular superoxide (O2• – ) by astrocytic NADPH oxidase. Astrocyte-secreted superoxide dismutase 3 (Sod3) converts O2• – to hydrogen peroxide (H2O2), which is imported into neurons. Sod3 activity requires copper ions, which are supplied by neuronal amyloid precursor protein.
This redox-based communication is disrupted by amyloid-β, a mechanism that potentially underlies cognitive deficits in Alzheimer’s disease.
The authors show that that human amyloid-β peptide, implicated in Alzheimer’s disease, inhibits the nAChRα7 astrocytic cholinergic receptor and impairs memory formation by preventing H2O2 synthesis.
https://www.nature.com/articles/s42255-024-01189-3
https://sciencemission.com/Astrocyte-to-neuron-H2O2-signalling