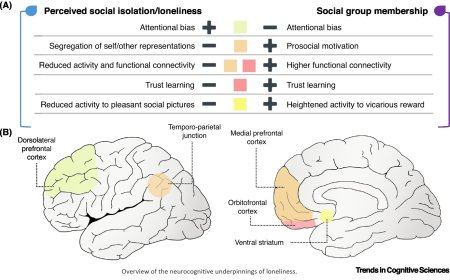
Biosensor to track burden in Escherichia coli
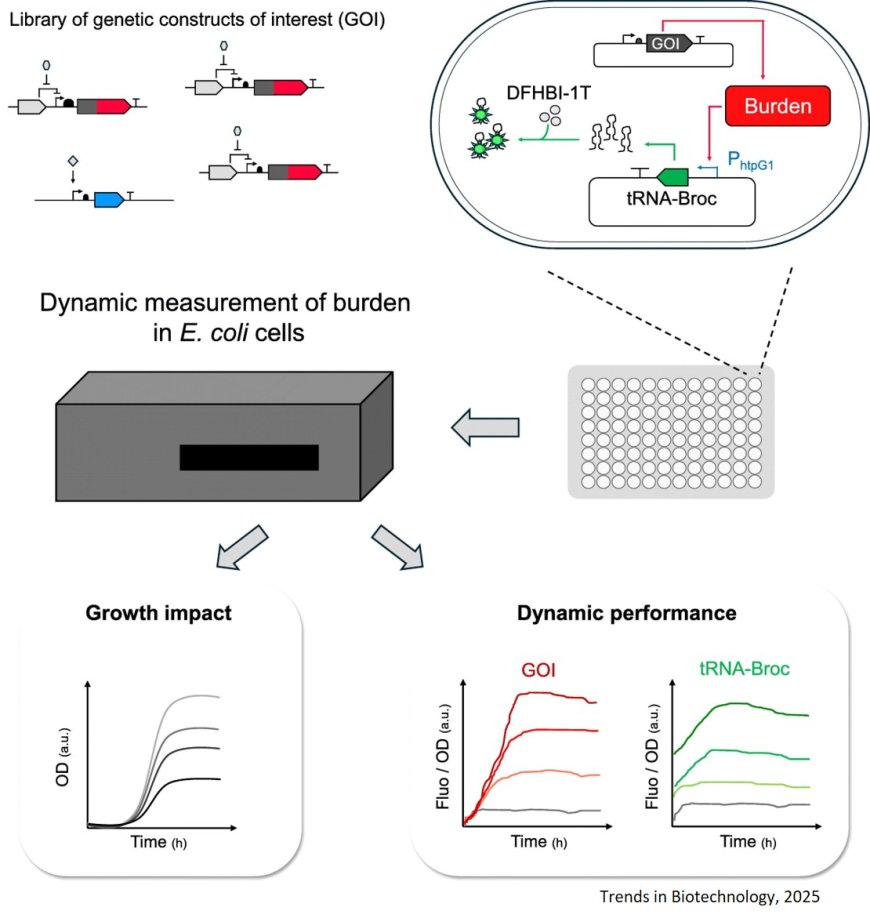
The researchers developed a fluorogenic RNA aptamer-based burden biosensor in Escherichia coli capable of informing on the burden of different genetic constructs via dynamic fluorescence readout.
They characterized a library of Pepper and Broccoli aptamers and highlighted that aptamer relative fluorescence strength is dependent on promoter, host and growth context.
The authors revealed that aptamer expression impacts Escherichia coli, leading to decrease growth in an RNA-scaffold-dependent manner, calling for caution in adopting these aptamers for applications in live cells.
They also tested a library of burden biosensors and showed the tRNA-Broc biosensor capable of reporting on the burden imposed by different expression levels and different genetic constructs.
The biosensor developed here quickly responded to burden and enabled identification of best-performing genetic variants with reduced burden providing a tool for improved engineering in Escherichia coli.
https://www.cell.com/trends/biotechnology/fulltext/S0167-7799(25)00222-7
https://sciencemission.com/biosensor-to-track-burden-in-Escherichia-coli