Botulinum neurotoxin binding of synaptic vesicle glycoprotein 2
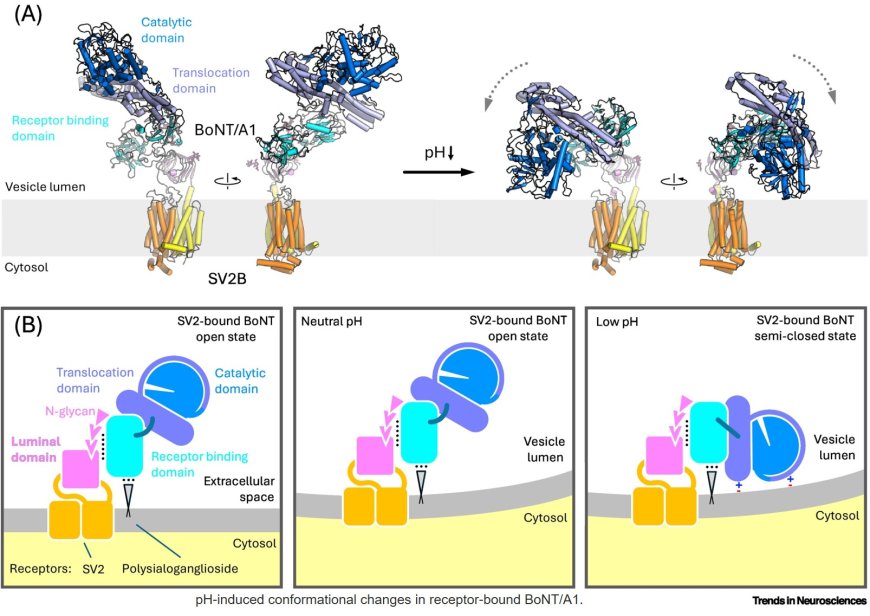
Cryo-electron microscopy (Cryo-EM) has enabled the high-resolution structural characterization of synaptic vesicle glycoprotein 2A (SV2A) and SV2B proteins, which serve as targets for anticonvulsant drugs and as receptors for several botulinum neurotoxins (BoNTs).
Structural analyses have revealed the molecular details of how anticonvulsant drugs bind to SV2A, as well as how these interactions can be regulated through allosteric modulation.
A conserved binding mode between BoNT/A subtypes and SV2 proteins has been identified that is not conserved in other BoNT serotypes.
Conformational changes observed in BoNT subtype A1, commonly known as Botox, both in solution and upon binding to SV2 receptors, have significant implications for toxin translocation.
https://www.cell.com/trends/neurosciences/fulltext/S0166-2236(25)00216-4
https://sciencemission.com/conformational-changes-in-receptor-bound-BoNTA1