Role of serine in human brain cancer growth
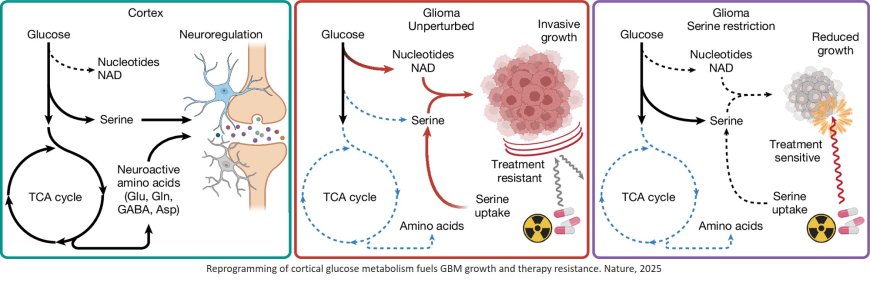
Cancer cells alter metabolic programs to support uncontrolled growth and proliferation.
Normally, cortex robustly takes up glucose, which it uses to fuel the TCA cycle and synthesize neuroregulatory metabolites including serine, glutamate, glutamine, GABA and aspartate.
Brain tumors upregulate the uptake of environmental serine and reduce the fraction of glucose incorporated into the TCA cycle and glucose-derived neurotransmitter synthesis. Tumors also reroute glucose-derived carbons to synthesize nucleotides and NAD/NADH, used to drive tumor growth and resistance to chemoradiation.
Restriction of dietary serine forces multiple gliomas to reroute glucose carbon towards serine synthesis, which decreases nucleotide and NAD/NADH levels, slows tumor growth and sensitizes tumors to chemoradiation.
https://www.nature.com/articles/s41586-025-09460-7
https://sciencemission.com/glucose-metabolism-fuels-glioblastoma