Caudal ganglionic eminence-derived inhibitory neuronal production and function
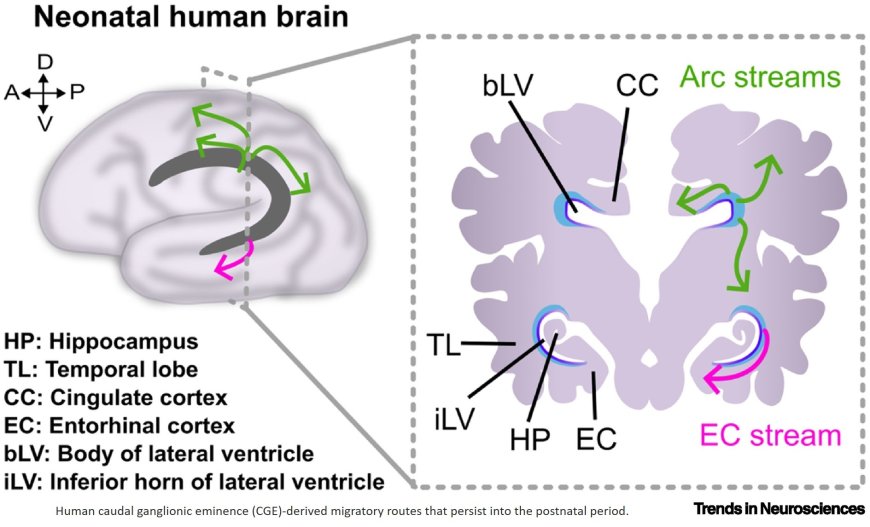
The caudal ganglionic eminence (CGE) is a transient neurogenic niche in the ventral embryonic brain containing neural stem cells, or radial glia (RG), in the ventricular zone and intermediate progenitors in the subventricular zone.
The CGE generates 30–50% of all inhibitory neurons depending on cortical region and species.
Progenitors in the CGE produce molecularly distinct inhibitory neurons that populate a variety of brain regions, including the cortex, hippocampus, and amygdala.
The CGE contains spatially segregated sub-compartments with distinct cytoarchitectural organization and gene expression profiles.
CGE progenitors have been implicated in the disease progression of tuberous sclerosis complex (TSC) and CGE-derived neuronal subtypes have been tied to roles in a variety of conditions, including schizophrenia and autism spectrum disorder.
https://www.cell.com/trends/neurosciences/fulltext/S0166-2236(25)00137-7
https://sciencemission.com/caudal-ganglionic-eminence-derived-inhibitory-neurons