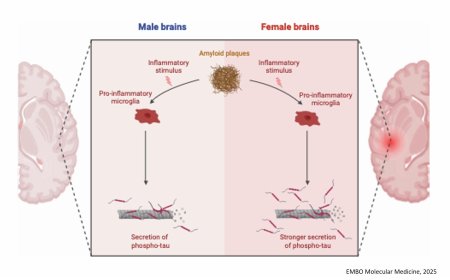
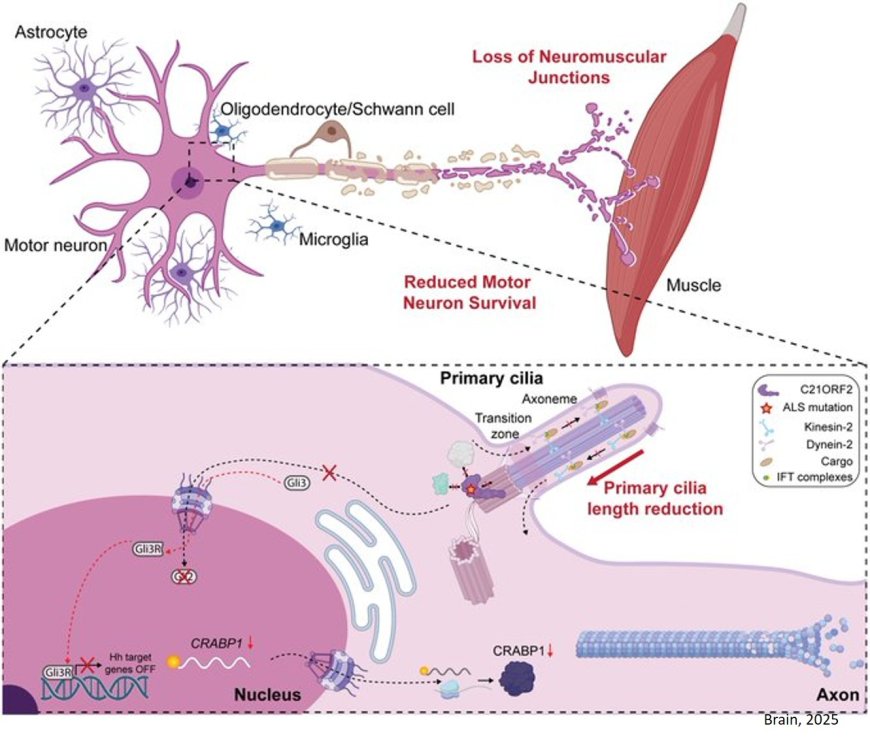
Cilia dysfunction in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) is a neurodegenerative disease, but the underlying disease mechanisms remain incompletely understood.
ALS has been linked to C21ORF2 gene mutation, and the researchers find that primary cilia are dysfunctional in the disease with reduced ciliary frequency and length in human patient-derived mutant C21ORF2 motor neurons.
C21ORF2 is located at the basal body of the primary cilium, and mutations associated with ALS alter this localization.
The researchers also demonstrate that ciliary defects were associated with a reduced ability of neuromuscular junction formation.
Overexpression of C21ORF2 in mutant C21ORF2 motor neurons rescued the ciliary frequency and length, and neuromuscular junction formation.
https://academic.oup.com/brain/article/148/3/803/7928515
https://sciencemission.com/C21ORF2-mutations-and-primary-cilia-dysfunction