Controlling behavior through interacting corticobasal ganglia-thalamocortical loops
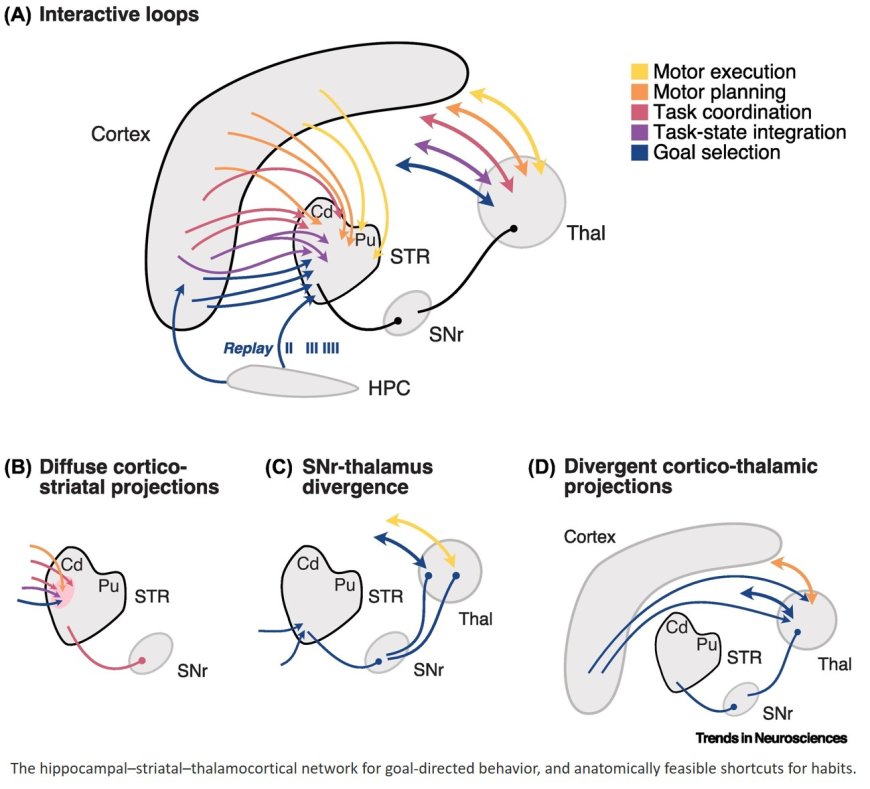
Understanding the interplay between goal-directed and habitual behavior is crucial for neuroscience and AI.
Traditional models assume distinct systems. The researchers in this publication highlight emerging anatomical evidence that suggests an integrated framework based on crosstalk between cortex-basal ganglia-thalamocortical loops.
Based on anatomical findings, we suggest that habitual responses arise from trained shortcut connections between those loops, facilitating automaticity while reducing computational load.
Striatal hubs for context integration share similarities with the self-attention mechanism in Transformer neural networks, the state-of-the-art in machine learning.
This framework unifies cognitive maps in the hippocampus with interacting cortex-basal ganglia-thalamocortical loops. In this framework, hippocampal replay contributes to goal selection and learning in the ventral striatum and medial prefrontal cortex.
https://www.cell.com/trends/neurosciences/fulltext/S0166-2236(25)00192-4
https://sciencemission.com/Interacting-corticobasal-ganglia-thalamocortical-loops