Mechanism of ESCRT-III inhibition by α-synuclein aggregates
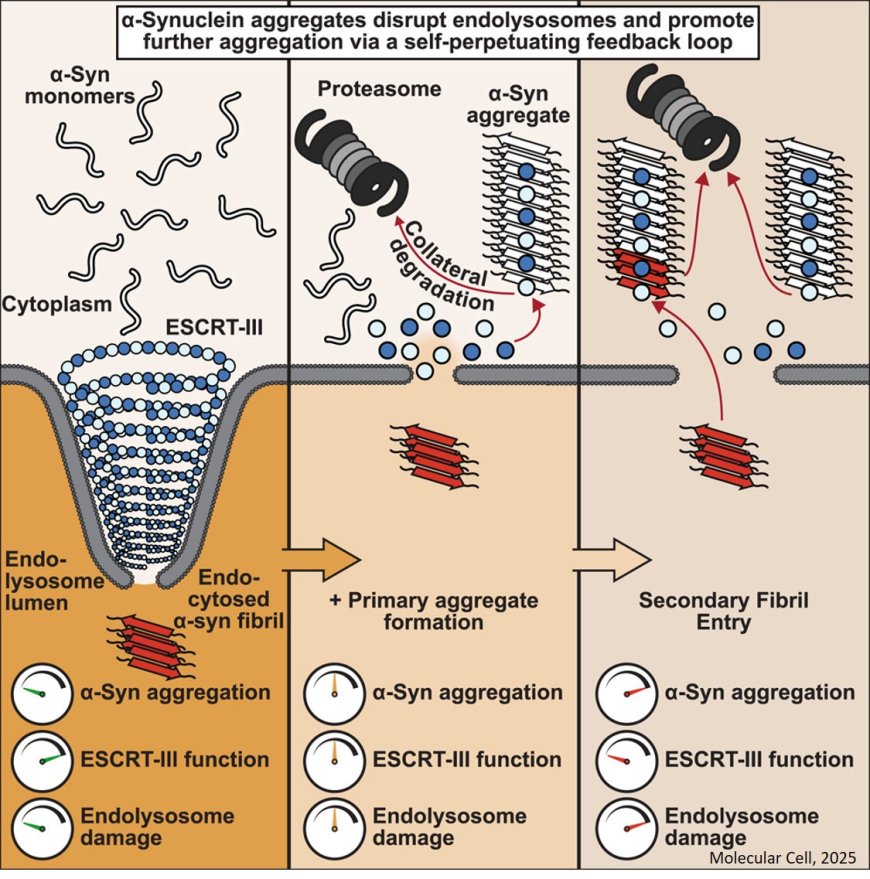
Neurodegeneration-associated aggregates, such as α-synuclein inclusions in Parkinson’s disease, often contain ESCRT-III proteins. ESCRT-III system are involved in endolysosome membrane repair.
The researchers show that α-synuclein fibrils interact with a conserved α-helix in ESCRT-III proteins and sequesters ESCRT-III subunits and triggers their proteasomal destruction in a process of “collateral degradation.”
Loss of ESCRT function compromises endolysosome membranes, thereby facilitating escape of aggregate seeds into the cytoplasm, facilitating a “second wave” of templated aggregation and ESCRT-III sequestration. This cascade functionally depletes ESCRT-III to initiate a toxic feedback loop.
https://www.cell.com/molecular-cell/fulltext/S1097-2765(25)00707-5
https://sciencemission.com/%CE%B1-Synuclein-aggregates-inhibit-ESCRT