FAPs in muscle physiology
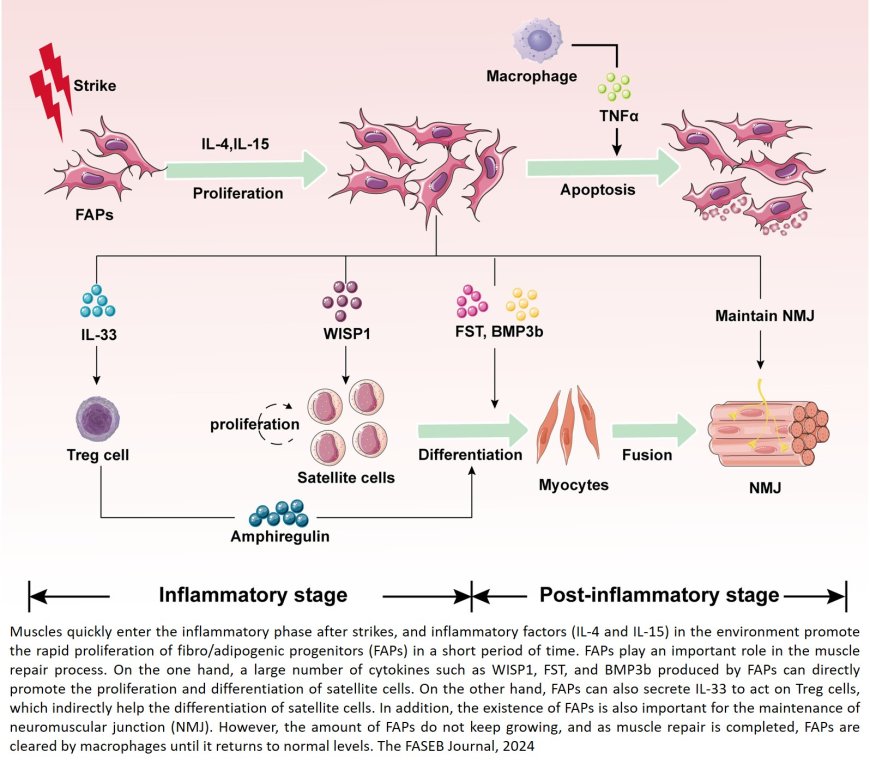
Muscle weakness in mobility disorder patients show persistent muscle inflammation, loss of muscle fibers, fat infiltration, and interstitial fibrosis.
The researchers have identified an interstitial progenitor cell, fibro/adipogenic progenitors (FAPs) during the transition from normal muscle microenvironment homeostasis to muscle microenvironment imbalance caused by muscle damage diseases.
FAPs can differentiate into fibroblasts, adipocytes, osteoblasts, and chondrocytes and also involved in the generation of extracellular matrix, regulate muscle regeneration, and maintain neuromuscular junction.
Alterations in FAPs my cause pathological changes in muscles and the researchers have identified appropriate signaling targets for FAPs to improve and even treat muscle damage diseases.
The authors in this review discuss muscle microenvironmental homeostasis and how it is disturbed during abnormal differentiation and apoptosis of FAPs and the strategies to inhibit the abnormal pathological changes in muscle damage diseases and improve muscle regeneration.
https://faseb.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1096/fj.202400381R
https://sciencemission.com/FAPs-orchestrate-homeostasis-of-muscle-physiology-and-pathophysiology