Glucocorticoid receptor modulator design and development
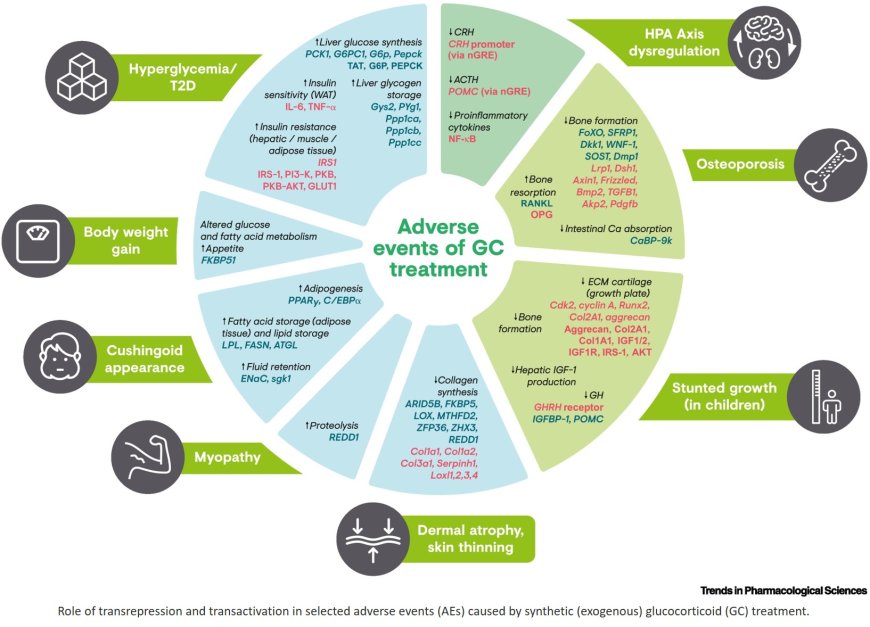
Glucocorticoid (GC) receptor (GR) transrepression and transactivation were considered distinct drivers of GC anti-inflammatory effects and adverse effects (AEs), respectively.
Current evidence indicates that both transrepression and transactivation explain GR-mediated GC effects, modulated by several regulatory factors.
Research continues to focus on retaining anti-inflammatory effects while minimizing AEs through the development of novel GR modulators (GRMs).
Approaches investigated to shift the benefit–risk ratio include designing dissociated steroids, selective GR agonists and modulators (SEGRAMs), and GRM–antibody–drug conjugates.
Vamorolone, a novel dissociated steroid approved for Duchenne muscular dystrophy, provides proof of concept that some separation of transrepression from transactivation is achievable.
Technological advances provide novel insights into GR structure, GR ligand binding, and the GR-DNA complex, which will inform future GR ligand design.
https://www.cell.com/trends/pharmacological-sciences/fulltext/S0165-6147(25)00123-3
https://sciencemission.com/glucocorticoid-receptor-modulators