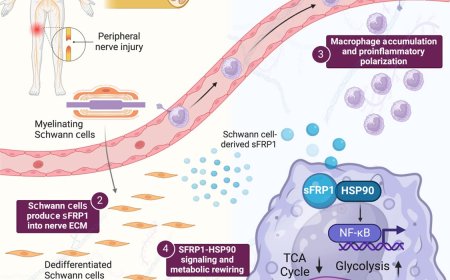
How Bifidobacteria reduce neuroinflammation in depressive brain
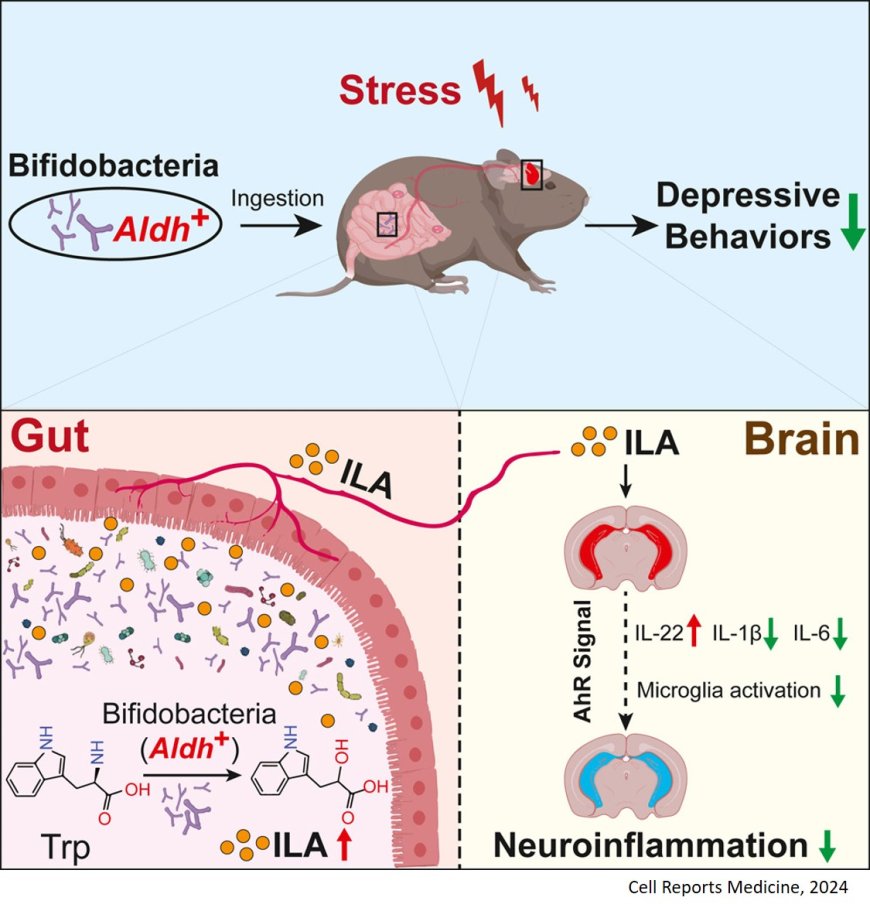
Although psychobiotics emerging as a promising solution for depression, the molecular mechanisms governing the neurobehavioral impact of psychobiotics remain elusive.
The researchers reveal that psychobiotic Bifidobacterium breve reverses the abnormal reduction of hippocampal indole-3-lactic acid (ILA) in depressed mice.
The study highlights the role of Aldh gene in ILA production by bifidobacteria and Aldh mutants nullified antidepressant effects compared to the wild-type strain. Also, the bifidobacteria with Aldh exhibit heightened antidepressant effects compared to the strains with low or no Aldh.
Antidepressant effects of bifidobacteria are mediated through AhR signaling, thus advancing the understanding of psychobiotics in mood disorder therapies.
https://www.cell.com/cell-reports-medicine/fulltext/S2666-3791(24)00545-7