Inflammatory muscle disease mechanisms and therapeutics
Treating idiopathic inflammatory myopathies (IIMs) remains challenging, highlighting the necessity for a deeper understanding of their pathophysiology to improve therapeutic approaches.
Recent studies have highlighted the pathogenic roles of myositis-specific antibodies and interferon pathways in IIM, paving the way for the development of new targeted therapies, such as chimeric antigen receptor T cells and Janus kinase inhibitors.
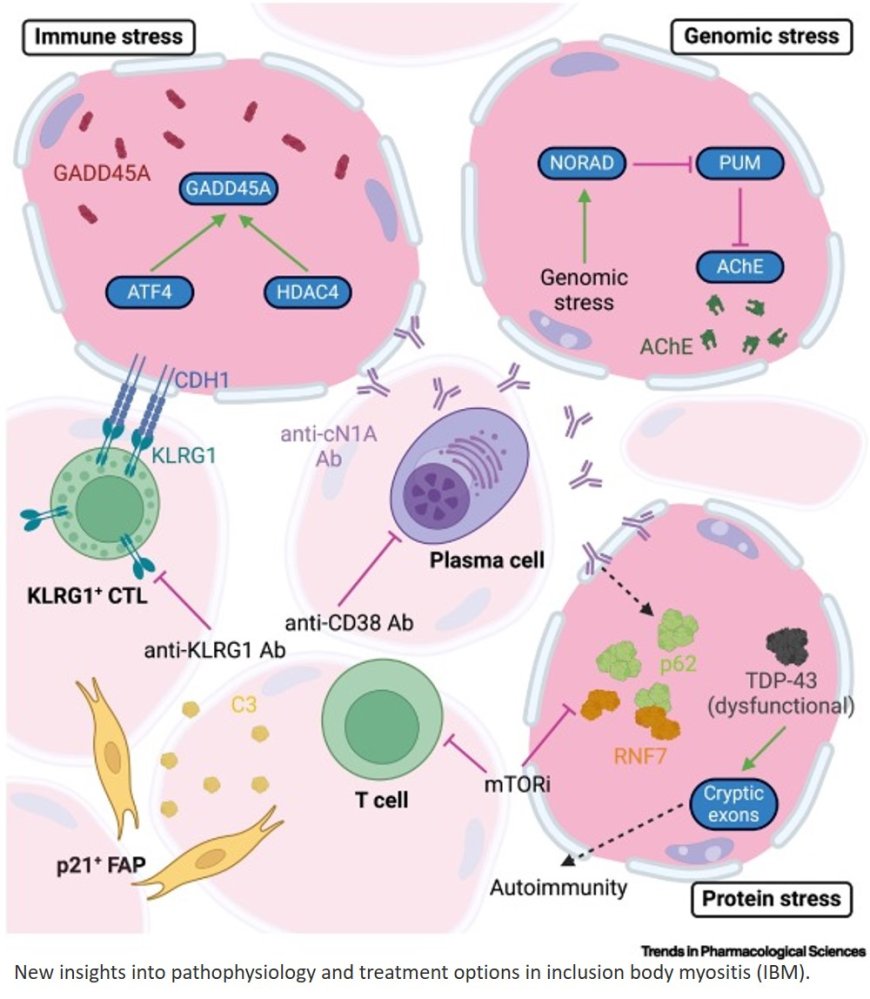
The identification of highly differentiated T cells and their role in inclusion body myositis (IBM) has led to the development of promising targeted therapies, which are currently undergoing clinical trials.
Recent discoveries on myofiber degeneration in IBM, including the role of cryptic exons and the increased susceptibility of type 2 myofibers, have revealed critical pathways in disease progression, presenting new potential therapeutic targets.
Advanced transcriptomic technologies have improved diagnostic accuracy and facilitated the identification of potential therapeutic targets in IIMs. Specific gene expression patterns now assist in classifying IIM subtypes and could guide personalized treatment approaches.
https://www.cell.com/trends/pharmacological-sciences/fulltext/S0165-6147(25)00005-7